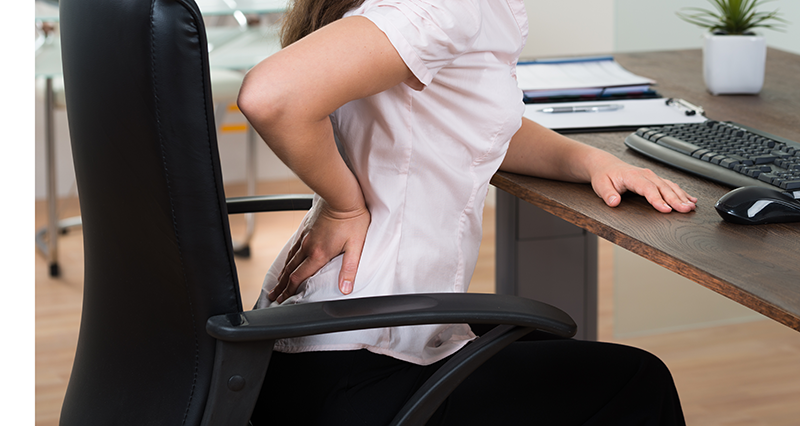
If you sit at a desk for work for long periods and suffer from back pain, the cause of your pain might be the way you are sitting or how your desk is set up. The first line of preventing back pain at work is to carry out an ergonomic assessment. This can either be done by a health and safety officer at your work or by yourself.
Ergonomic assessment
Ergonomics is the process of optimising human well-being and performance, essential in preventing back pain at work. This involves assessing and improving safety, comfort, productivity, and ease of use of equipment.
In the workplace, ergonomics usually relates to the employee’s workstation, where a high number of cases are desk and computer.
Ergonomists assess a workstation for suitability to the employee and the job, and in their quest to prevent back pain at work, they make changes to the desk, chair, computer, and other equipment positions, to make the set-up more user-friendly. They may also introduce new pieces of equipment, such as wrist supports and footrests.
How should my desk be set up?
In order to set up your desk, chair, and computer correctly, and avoid developing poor posture and injuries, follow these simple steps:
Buy Back Supports
Chair
To start with preventing back pain at work, ensure you have a good chair with lumbar support, head, and armrests. Adjust the height of your chair so that when sitting at your desk the following are true:
1. Your thighs are supported by the chair when your feet are flat on the floor and there is a right angle at the knee
2. When you place your fingers on the middle row of keys, your forearms rest on the desk.
3. There is no bend at the wrist (i.e. a straight line from your wrist, across to your hand and fingers).
4. Your elbows are supported by the armrests when your forearms are rested on the table. Some chairs have adjustable armrests which you can move to the right height for you. Those without adjustable armrests can be raised by wrapping foam around the rest until it is the right height and taping it in place.
5. You may require a footrest under your feet if your desk is too high to have your forearms supported on the desk and feet flat.
Adjust the back support so that when you sit upright the lower back is supported fully. If the curvature of the chair does not match your back you may require additional lumbar support Ensure there is at least a 2″ (5cm) space between the back of the knee and where the chair seat stops.
Monitor
- Now that your chair is correctly positioned, adjust the height of your computer monitor. The top of the monitor should be at eye level, meaning you keep your head straight and look down slightly with your eyes. Monitor height can be adjusted using boxes, books etc.
- Check that the monitor is directly in front of you.
- Move the chair close to the desk until you are in a position where the elbows (when the forearms are resting on the desk) are directly under the shoulders.
- From this position, the screen should be 22-26″ (55-65cm) away from you. If not, position it at this distance. If you had it closer than this you may need an eye examination.
Desk
- Your desk should be kept clutter-free to allow for all of your equipment to be positioned correctly.
- If when your chair is positioned correctly your desk is too low or high, consider purchasing a new desk. This may seem like drastic and expensive action but it may save you hefty treatment bills later down the road!
Mouse and other equipment
The other equipment on your desk should also be positioned to provide maximum comfort and practicality:
1. Position your mouse as close to you as you can whilst maintaining the elbow beneath the shoulder, the elbow supported on the armrest and the wrist on the desk.
2. When using your mouse, move the arm whilst keeping the forearm rested on the desk. Don’t use the wrist to move the mouse as this can lead to RSI.3. Position your phone and any other equipment which is not permanently in use to the left-hand side, within arms reach.
Kinesiology Taping for Low Back
A simple Kinesiology taping technique demonstrated by Sports Physiotherapist Neal Reynolds can help relieve low back pain.
This kinesiology taping technique for the back is designed to deactivate the muscles in the low back helping to relax them.