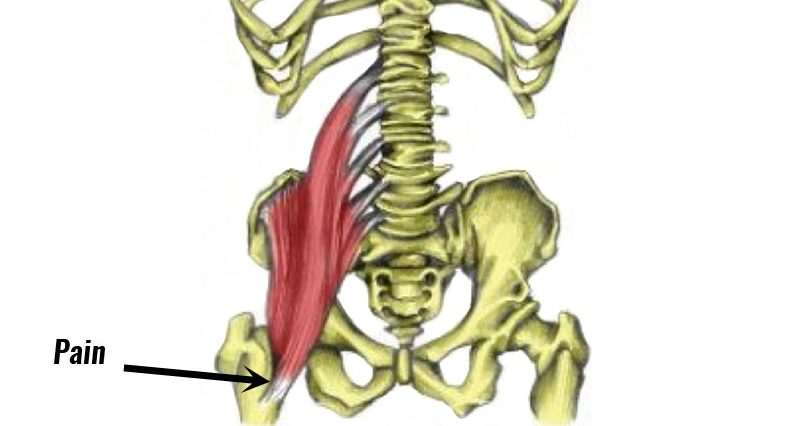
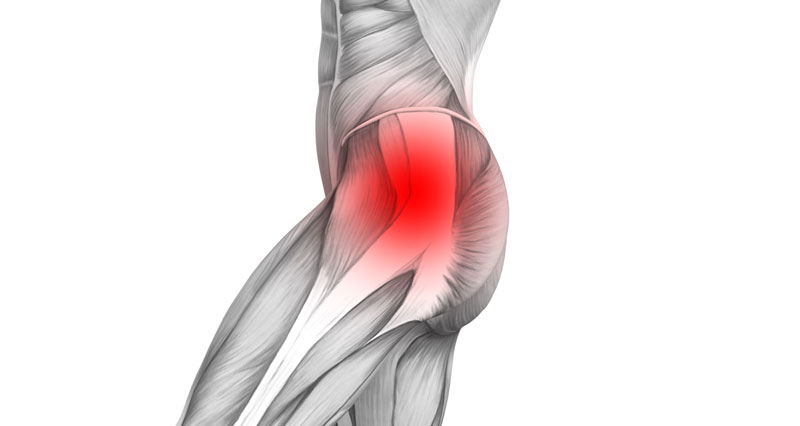
Iliopsoas bursitis and Iliopsoas tendon inflammation have similar symptoms of gradual onset pain, deep in the groin. The bursa is a small sack of fluid that reduces friction between the tendon and bone.
Symptoms
Iliopsoas bursitis symptoms and iliopsoas tendon inflammation have similar symptoms and may be difficult to distinguish between the two.
- Typically pain is felt at the front of the hip and groin, which is described as a deep pain in the groin.
- Pain may radiate down to the knee or even into the buttocks.
- A snapping sensation may be felt in the hip.
- In the mornings, pain and stiffness could be felt which eases as your body gets warmed up. But gets worse as activity increases.
Differentiating iliopsoas pain from other groin pain such as a groin strain, or ‘Gilmore’s groin‘ can be done by palpating (feeling) the muscle and by assessing pain and tightness when stretching the iliopsoas. Palpating the muscle is not easy as it is very deep in the abdomen, but an experienced therapist should be able to find the muscle by passively elevating the leg whilst palpating.
Thomas test
The Thomas test can be used to assess tightness or pain in the Iliopsoas muscle.
The patient lies on their back, pulling one knee up as high as it will go. The thigh of the free leg should be horizontal.
If it rides up, this indicates possible tight hip flexor muscles (Rectus femoris or Iliopsoas). The shin of the free leg should hand vertically. If not then this may indicate tight Quadriceps muscles.
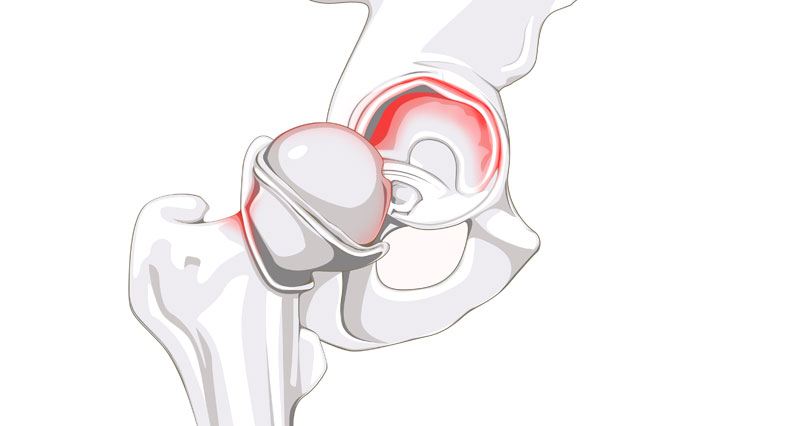
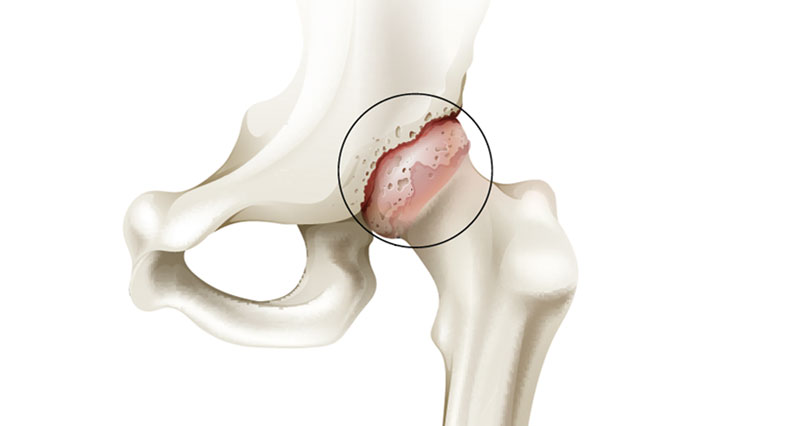
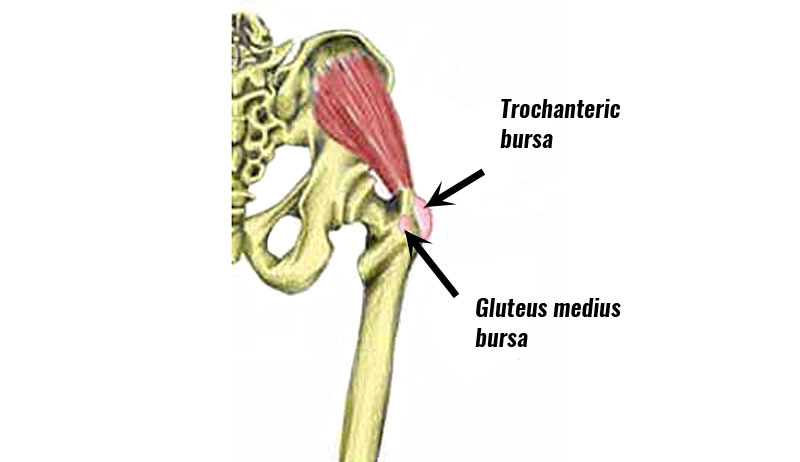
Iliopsoas bursitis causes & anatomy
The iliopsoas muscle is a large powerful muscle that flexes the hip (lifts the knee up). It is the most powerful hip flexor muscle and originates from the bottom five lumbar vertebrae and inserts into the thigh bone (femur). A bursa is a small sack of fluid that sits between a tendon and the bone to help reduce friction and lubricate the movement. Overuse can cause either the tendon (Iliopsoas tendonitis) or the bursa (Iliopsoas bursitis) to become inflamed. Repetitive rubbing of the tendon against the bursa will cause it to become inflamed.
In particular, athletes involved in kicking sports that place repetitive, one-sided strain on the muscle are more prone to iliopsoas injuries as are people who perform repetitive activities such as running or swimming.
Although overuse is the main cause of Iliopsoas bursitis, a big contributor to the development of iliopsoas bursitis is having tight hip flexor muscles. This puts more pressure on the front of the hip and causes more friction between the tendons and the bursa.
Treatment of Iliopsoas bursitis & tendonitis
What can the patient do?
Rest from repetitive activities or those that cause pain. If it hurts or makes things worse the following day then don’t do it. Continuing to train on an overuse injury will prevent healing and may cause the injury to become chronic and more difficult to treat.
Apply ice to ease pain and inflammation. Do not apply ice directly to the skin but wrap in a wet tea towel, or use a commercially available cold compression wrap which is likely to be more convenient and may apply compression to the area as well.
When pain allows, begin gentle stretching exercises for the hip flexor muscles.
What can a sports injury specialist do?
A doctor or sports injury professional may refer you for a CT scan or MRI if necessary to confirm the diagnosis. A doctor may prescribe or advise on anti-inflammatory medications such as Ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation, or both the tendon and bursa.
A sports injury professional will assess and advise on exercises to correct any muscle imbalances. This most frequently involves stretching the hip flexors and strengthening the abdominals and glutes. Muscle imbalances are especially common with Iliopsoas injuries from one-sided sports or kicking-type sports. An imbalance of the powerful Iliopsoas muscle can cause misalignment of the spine, making the athlete prone to further injuries. They may do a biomechanical assessment or gait analysis to determine if orthotic inserts for the foot may be required.
A Chiropractor or Osteopath may perform spinal manipulation or mobilization to align joints and release pressure on the nerves which might be a
Exercises for Iliopsoas bursitis/inflammation

Exercises to stretch the Iliopsoas muscle are important, as the muscle is often too tight.
This may be caused by repetitive strain through sport, but also a very common factor in tight Iliopsoas muscles is poor posture or sitting in a ‘chair-shaped’ position for prolonged periods as many of us have to at work or school.
Hip flexor stretch in kneeling is done by placing one foot in front of the other and dropping onto one knee.
Easy down to increase the stretch, hold for 10 to 20 seconds, and relax. Repeat 3 times and aim to repeat this routine 3 to 4 times throughout the day if possible (and pain-free).
An even better way of stretching the hip flexor muscles is with the help of a partner in the ‘Thomas test’ position lying on the back and allowing one leg to drop down. The partner then helps increase the stretch by gently applying force to increase the stretch.