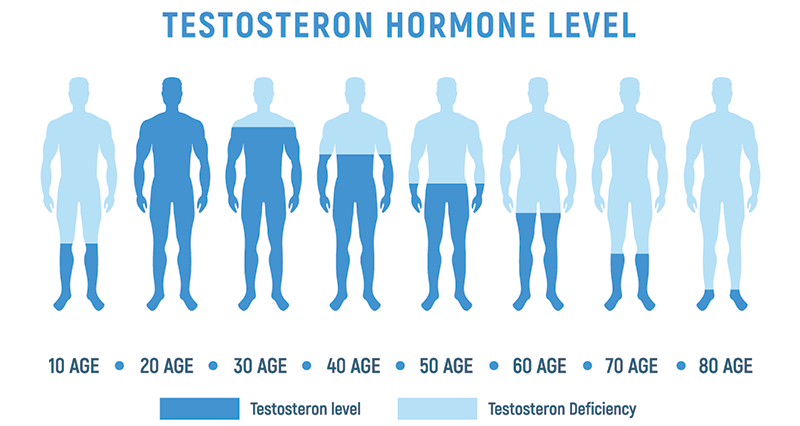
We all know how beneficial testosterone is when it comes to sports performance. There is a reason why taking substances to artificially increase your testosterone levels is banned in sports. However, as men age, their natural testosterone levels decrease. As a result, they often find maintaining or increasing strength more difficult.

Initially, the drop in T levels is gradual. However, after the age of 40, there is a more linear drop over time. If your testosterone levels are particularly low then this may impact your athletic performance and overall well-being. Here are six signs of low testosterone (hypogonadism):
Decreased Muscle Mass and Strength
Low testosterone causes reduced muscle mass and difficulty in maintaining or building strength, even with consistent training. Do you find you are putting the same effort in but are unable to lift the weights you used to? Or find yourself weaker if you miss a few weight training sessions? After exercise, the hormone helps repair micro-tears in the muscle tissue, leading to increased muscle size and strength over time.
Fatigue and Reduced Energy Levels
Persistent fatigue, decreased stamina, and a general lack of energy are also a sign your T levels are too low. Do you struggle to get through training sessions, either because you are too tired, or simply lack the spark you had years ago? Testosterone stimulates the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to tissues throughout the body. Better oxygen delivery improves muscle function and endurance, reducing feelings of tiredness and fatigue. Additionally, testosterone influences mood, motivation, and mental clarity. Low testosterone can lead to depressive symptoms, lethargy, and a lack of focus, all of which contribute to a sense of fatigue.
Reduced Recovery Time
Prolonged muscle soreness and slower recovery after exercise or injury could indicate declining testosterone levels. Testosterone plays a significant role in exercise recovery, primarily due to its anabolic (muscle-building) properties. It enhances muscle protein synthesis, the process where the body repairs and builds new muscle fibres after exercise. Also, it helps reduce the amount of muscle damage, enabling quicker repair and less muscle soreness. Testosterone stimulates the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to muscles. Better oxygen delivery means muscles can recover more quickly from exertion and reduce feelings of fatigue. Testosterone also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Increased Body Fat
Particularly a shift in fat distribution toward the abdomen, even with regular physical activity. Testosterone influences how the body stores and uses fat, improving insulin sensitivity and metabolising fat. Higher levels of testosterone can shift the body’s preference towards storing less fat and using more of it for energy, especially around the abdomen. Testosterone helps balance other hormones in the body such as cortisol (a stress hormone) which contributes to fat gain.
Decreased Libido and Sexual Performance
A decline in sexual desire and performance can be related to lower testosterone levels. Testosterone is essential for stimulating the brain areas involved in sexual arousal and desire. It helps activate neurotransmitters that enhance sexual thoughts, fantasies, and the drive to engage in sexual activity.
Mood Changes
Testosterone significantly affects mood and motivation in men. It plays a role not only in physical health but also in mental and emotional well-being. Low testosterone levels (hypogonadism) have been linked to mood disorders, including depression, irritability, and anxiety. Studies have shown that men with low testosterone are more likely to experience symptoms such as sadness, fatigue, and a lack of interest in activities they once enjoyed.
Decreased Bone Density
Low testosterone can lead to weaker bones (osteoporosis), increasing the risk of fractures, which is crucial for ageing athletes. Testosterone plays an important role in maintaining bone density in men and women. It stimulates bone mineralization by promoting the activity of bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) and helps preserve bone mass by reducing bone resorption (breakdown).
Treatment For Low Testosterone In Men
If you suspect you have low testosterone based on these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper testing and evaluation. Blood tests confirm whether your testosterone levels are low or not.
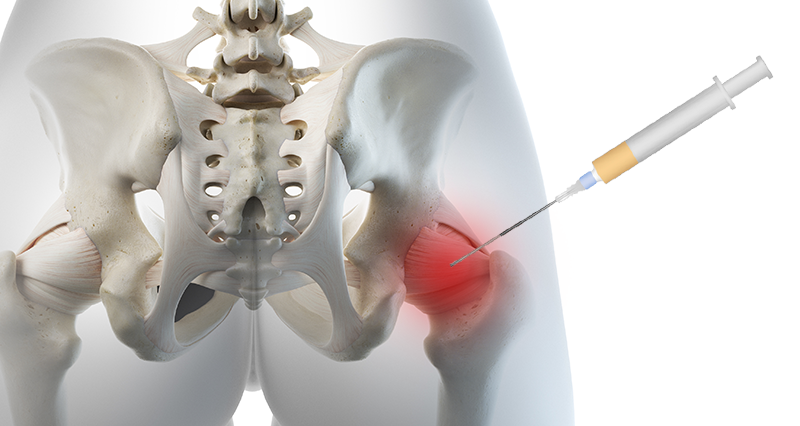
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a medical treatment used to increase testosterone levels in men who have low or deficient levels. It involves administering synthetic testosterone through various methods, including injections, gels, patches, or oral tablets. However, TRT is not permitted under WADA rules unless you have a medical exemption.
Athletes with legitimate medical conditions requiring TRT can apply for a Therapeutic Use Exemption (TUE). A TUE allows them to use banned substances, including testosterone if they can demonstrate a genuine medical need and follow WADA’s strict application process. So if you do opt for TRT then it is likely your competitive years are behind you now or you may find yourself with a drugs ban!