An eversion ankle sprain, medial ankle sprain, or deltoid ligament sprain is a tear of the ligaments on the inside of the ankle. It is not as common as an inversion ankle sprain and is often accompanied by a fracture of the fibula bone. Here we explain the symptoms, causes, and treatment for an eversion ankle sprain.
Eversion ankle sprain symptoms
You usually know you have sprained your ankle. With an eversion ankle sprain, your ankle rolls inwards. Signs and symptoms include:
- Immediate pain on the inside of your ankle.
- Swelling develops rapidly.
- Bruising may also appear later.
- Difficulty with weight-bearing and limited ankle mobility.
Imaging
An X-ray may be required to determine the extent of the injury and rule out fractures.
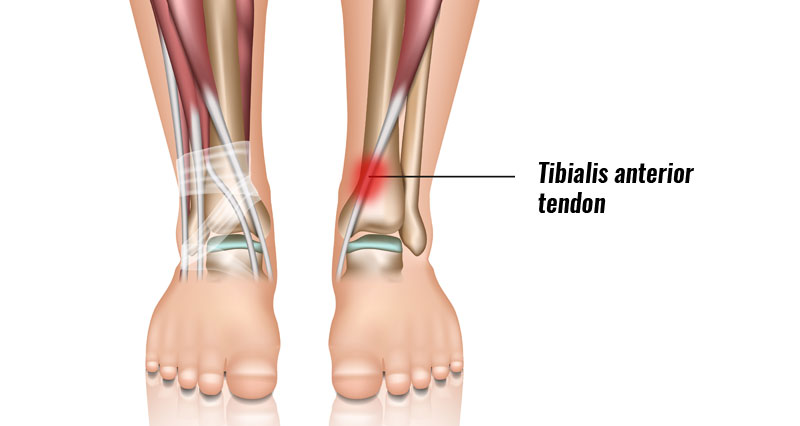
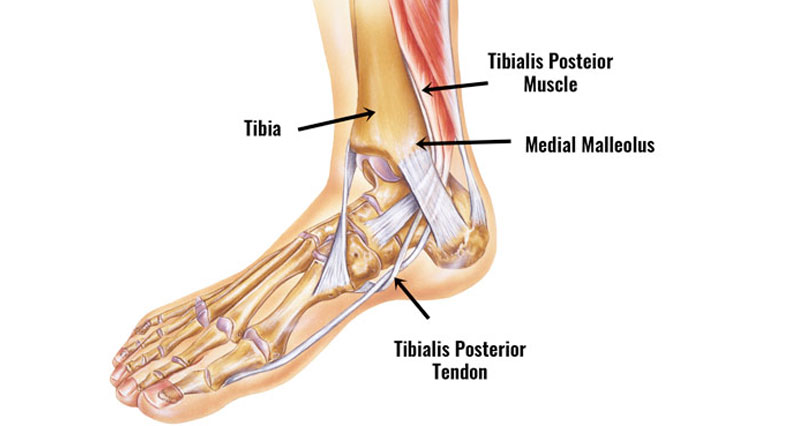
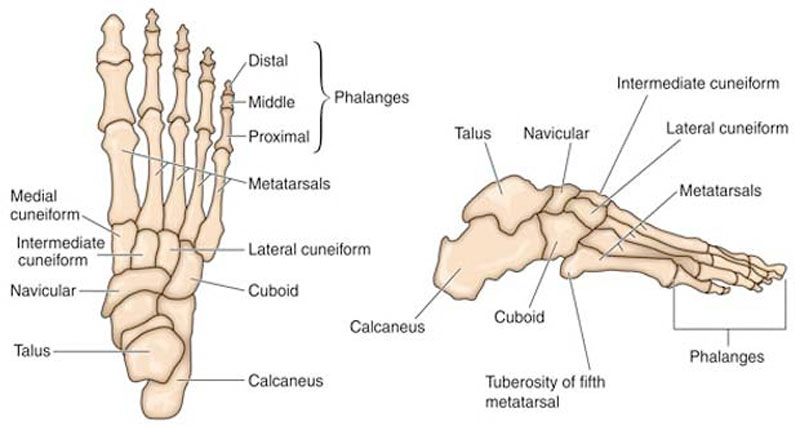
Anatomy
Ligaments hold the ankle joint together. They join bone to bone. The lateral ligaments are on the outside of the ankle and consist of the talofibular ligament and the calcaneofibular ligament.
The talofibular ligament joins the talus to the fibula, whilst the calcaneofibular ligament joins the calcaneus to the fibula.
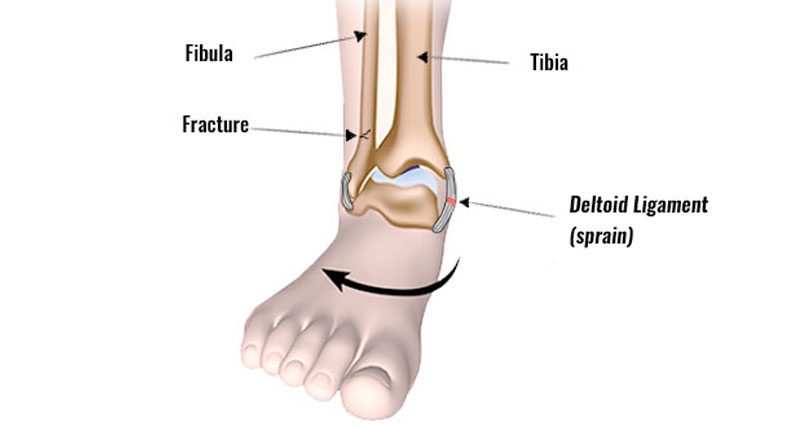
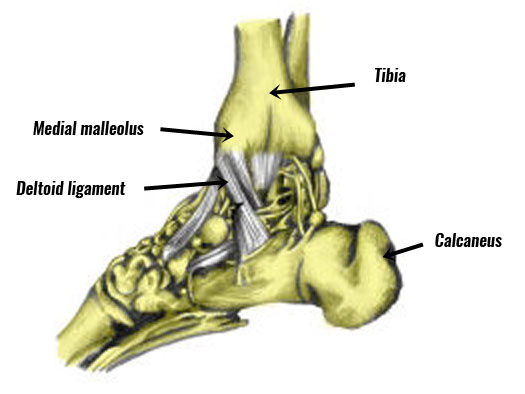
The medial ligaments on the inside of the ankle consist of the tibiotalar ligament, tibiocalcaneal ligament, and the tibionavicular ligament. They are known as the deltoid ligaments.
What is an ankle eversion sprain?
An eversion sprain is a tear of the deltoid ligaments, on the inside of the ankle.
These ligaments provide support to prevent the ankle from turning inwards or everting.
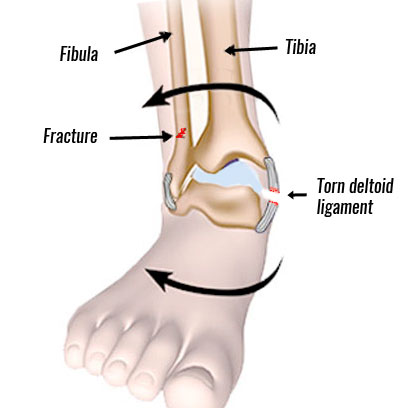
It is rare that the deltoid ligaments tear. This is because the fibula restricts the ankle from rolling in (everting). As a result, it is difficult for the deltoid ligaments to overstretch. Also, the medial ligaments are much stronger than the lateral ligaments on the outside.
If however, the fibula fractures then there is nothing preventing excess ankle eversion. Therefore, an eversion ankle sprain often occurs with a fibula fracture, called a Pott’s fracture.
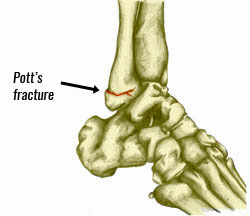
Other bones in the ankle such as the talus may also fracture during an eversion ankle sprain depending on the severity of the injury.
Treatment of medial ankle sprains
Initial treatment should involve applying the PRICE principles of rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Rest
Rest is important both immediately after injury as well as whilst the injury is healing. Continuing to walk or play while it is painful will increase swelling and slow the healing process. If you suspect a severe sprain or a fracture then seek immediate medical assistance.
Cold therapy
Apply ice or cold therapy immediately after the injury. Ice should not be applied directly to the skin. Wrap it in a wet tea towel, or use a commercially available hot and cold pack which are often more convenient.
You can apply cold for 10 to 15 minutes every hour for the first 24 to 48 hours. Then reduce the frequency as symptoms improve.
Compression & elevation
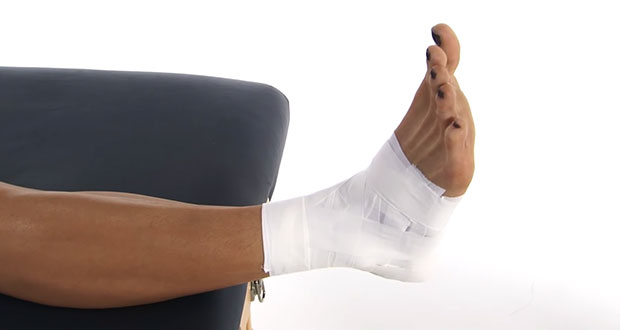
Compression with an ankle taping or compression bandage will protect the joint from further injury and help reduce swelling. Elevating the limb encourages the swelling and tissue fluids to flow away from the site of injury.

Zinc Ocide Sports Tape