Tinel’s test in the wrist assesses for the presence of irritated or compressed nerves, in particular, carpal tunnel syndrome. The carpal tunnel is a channel in the wrist through which nerves and tendons pass.
What is Carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve in the wrist becomes compressed. Various factors narrow the carpal tunnel, exerting pressure on the nerve. These factors include traumatic wrist injuries, repetitive strain injury (RSI), pregnancy-related fluid retention, use of vibrating machinery, congenital predisposition, and arthritis.

How to perform Tinel’s test for the wrist?
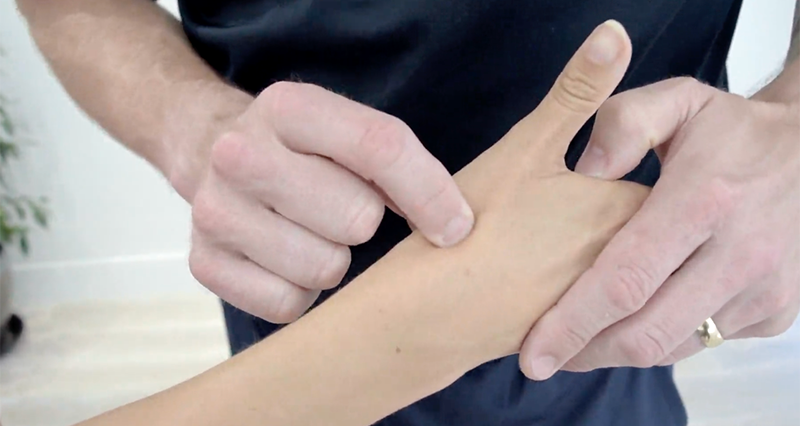
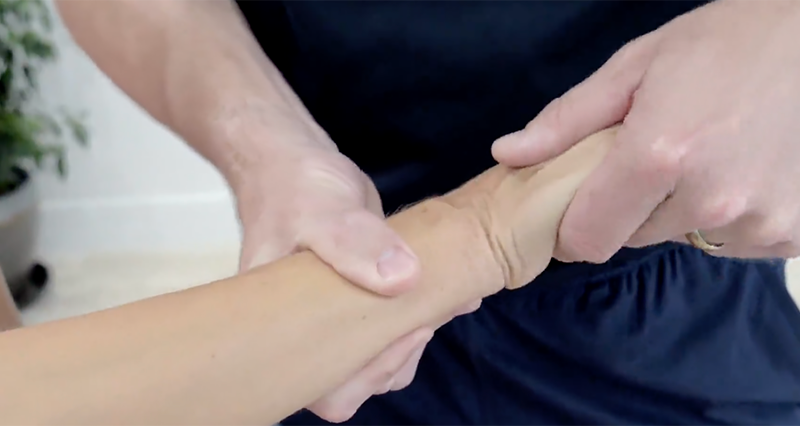
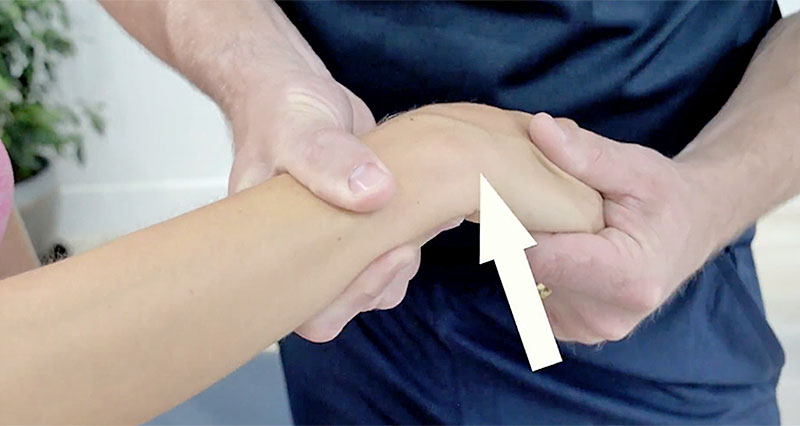
Firstly, position the patient seated or standing comfortably with their arm extended and palm facing upwards. Next, support the wrist with one hand and lightly tap or press along the course of the median nerve. This area is typically just above the wrist crease on the palm side of the hand. Observe the patient’s response to the tapping or pressure.

What is a positive Tinel’s test?
The test is positive if the patient experiences tingling, pins and needles sensation, or numbness radiating into the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger.

Considerations
A positive Tinel’s test or sign suggests potential nerve compression, such as in carpal tunnel syndrome. However, it’s important to note that a positive Tinel’s sign doesn’t confirm a specific diagnosis on its own. It is important to use this test in conjunction with other clinical assessments and diagnostic tests.
Overall, Tinel’s test is a simple yet effective way to help diagnose nerve compression or irritation in the wrist and guide further evaluation and treatment.