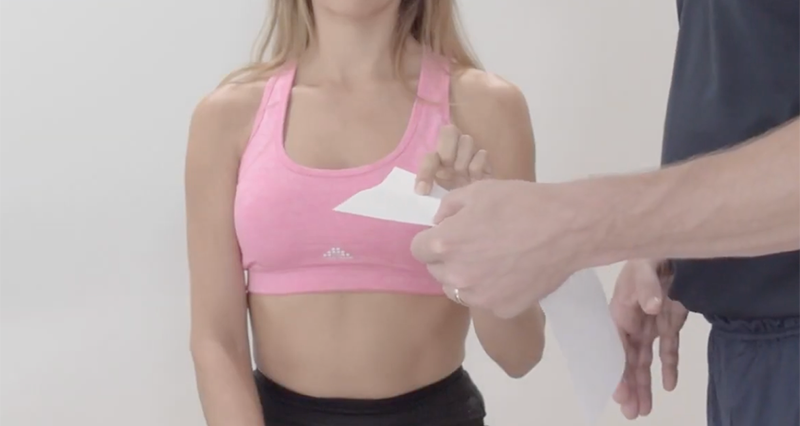
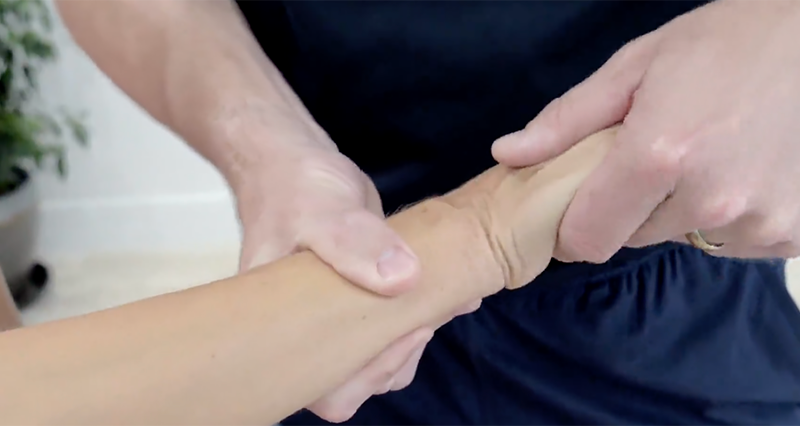
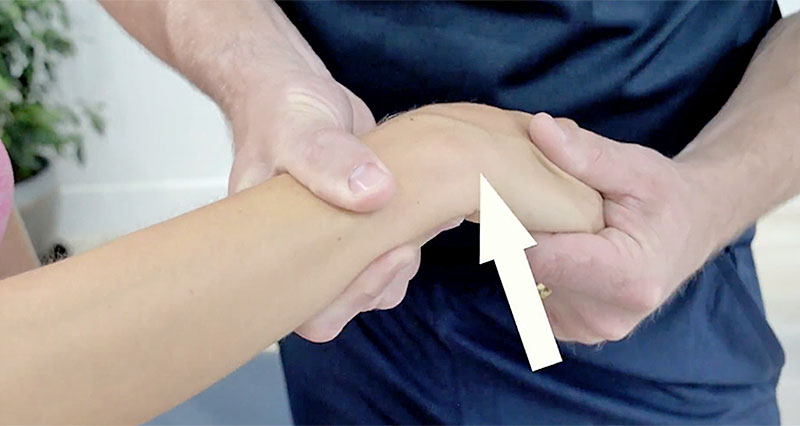
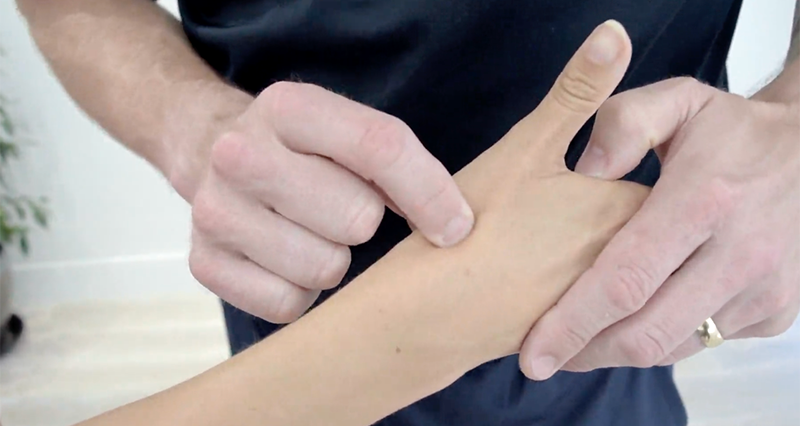
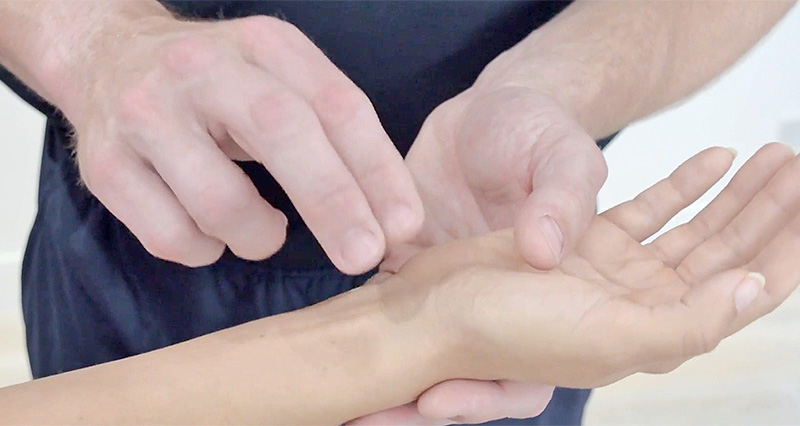
Finkelstein’s test, a clinical examination, diagnoses de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, a condition marked by inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. Consequently, these tendons facilitate thumb movement.
What is De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
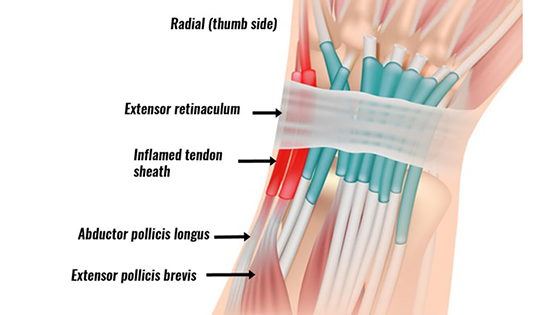
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis involves inflammation of the synovium or sheath surrounding two wrist tendons that attach to the base of the thumb. Additionally, it is a form of repetitive strain injury that worsens with sports or work-related activities.
The condition affects the abductor pollicis brevis and extensor pollicis longus tendons, which run through a wrist tunnel and attach to the thumb base. It commonly appears in racket sports like tennis, squash, or badminton, as well as in canoeing and bowling. Additionally, any activity involving repetitive wrist movements can trigger this condition.
How the Finkelstein’s test is performed
First, the patient forms a fist with their fingers wrapped over the thumb. Then, someone holds the patient’s forearm steady to prevent movement. Finally, the patient moves their wrist towards the little finger side, known as ulnar deviation, following instructions.
What is a positive Finkelstein’s test?

If you feel pain along the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist, especially where the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis (the tendons responsible for thumb movement) pass through, it suggests a positive Finkelstein’s test. This typically indicates irritation or inflammation, known medically as de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
Considerations
It’s important to note that although a positive Finkelstein’s test strongly suggests de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, doctors might need additional diagnostic tests or imaging studies for confirmation. Treatment options can also vary based on the severity and individual circumstances of the condition.