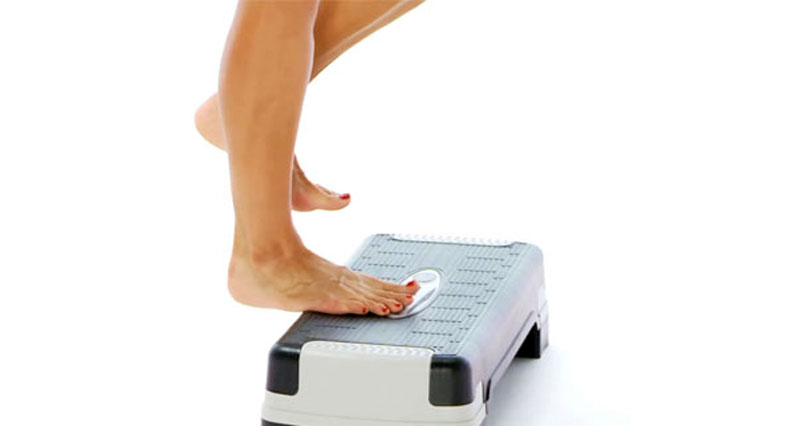
A total rupture of the Achilles tendon is a complete tear of the large tendon at the back of the ankle. It typically affects men over the age of 40. It is not always obvious if you have completely torn your Achilles tendon, but if you have, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Achilles tendon rupture symptoms
Symptoms of a torn Achilles tendon include:
- Sudden sharp pain in the Achilles tendon at the back of your ankle
- Often described as being struck physically on the back of your ankle
- You may hear a loud snapping noise or bang at the time of injury
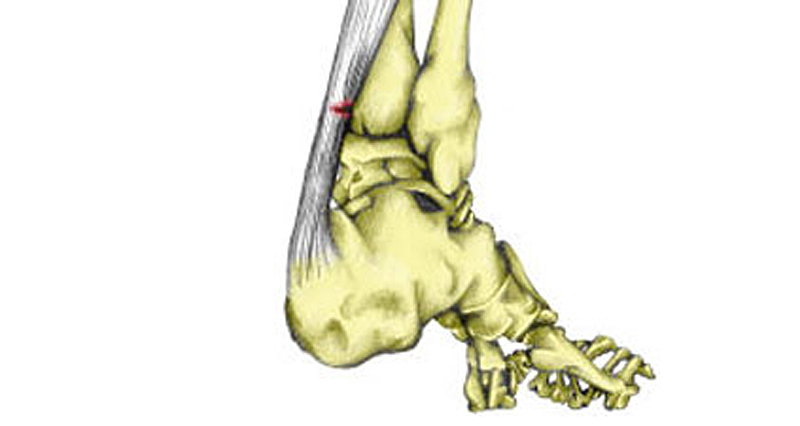
- You may see or feel a gap of 4 to 5 cm in your tendon immediately after injury (less obvious as swelling increases)
- Loss of function and strength in the injured ankle
- You will most likely be limping
Sometimes patients can walk or even continue playing. This is because other muscles which plantar flex the ankle compensate.

Buy Achilles Straps
Assessment & diagnosis
There are four key tests to help diagnose a complete rupture of the Achilles tendon:
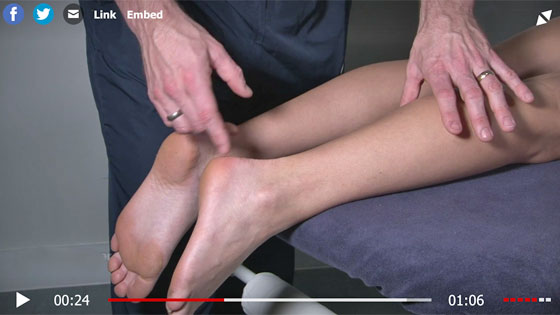
1. Lie face down with your feet hanging over the edge of a table or therapy couch. The injured leg may hang directly down, compared to the non-injured one.
2. Is there a gap of approximately 3 to 6 cm in the Achilles tendon directly after an injury? If there is too much swelling then this is not always obvious.
3. Reduced strength? For example, the patient will be unable to point their foot downwards against resistance or go up on top toes.
4. Thompson’s squeeze test is performed by squeezing the calf muscles at the belly of the muscle. If the foot does not move then this may indicate a complete rupture.
What is a complete rupture of the Achilles tendon?
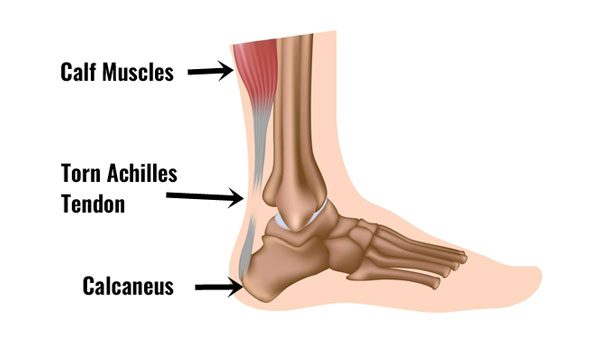
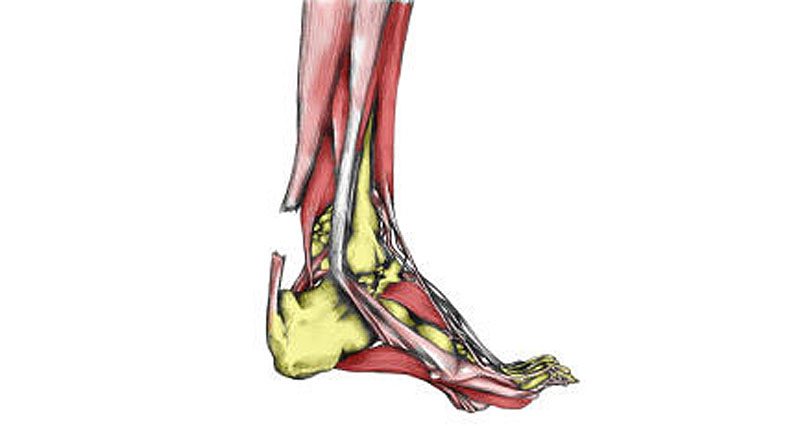
A torn Achilles is simply a tear of the Achilles tendon. It can be a partial rupture or a total rupture. A total rupture is 10 times more common in men than in women.
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg and inserts at the back of the heel or calcaneus bone. Huge forces transmit through the tendon when running and jumping. A thin sheath surrounds the tendon itself.

Buy Kinesiology Tape
What causes a torn Achilles?
Typically it occurs 30 to 40 minutes into a period of exercise, rather than at the start of a session. Nearly always it results from either a sudden explosive movement or when forcibly bending the foot upwards (known as dorsiflexing).
A rupture may (but not always) follow long-term tendon pain which a patient may have put up with, or ignored for some time. Many patients are able to continue to function following an Achilles rupture due to other lower leg muscles compensating, although the injured leg is significantly weaker.
Read more on preventing Achilles ruptures.
Treatment for a total rupture of the Achilles tendon
If you suspect a total rupture of the Achilles tendon apply the PRICE principles (protection, rest, ice/cold therapy, and elevation. Seek medical attention immediately.
Do I need surgery for an Achilles rupture?
If you are unlucky enough to suffer a complete rupture of your Achilles tendon then you have two choices:
- Conservative treatment (without surgery)
- Surgery to repair the torn tendon
Conservative treatment
The conservative route involves initial immobilization to allow the tendon to heal, followed by strengthening and improving flexibility.
Read more on Achilles tendon rupture rehabilitation.
Surgery
Whether to opt for surgery for a complete rupture of the Achilles tendon is based on various factors, including the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. In most cases, Achilles tendon surgery is the preferred choice. Often, the sooner this takes place the higher the chances of success. A full rehabilitation program is necessary following surgery with the patient being out of competition for between 6 and 12 months.