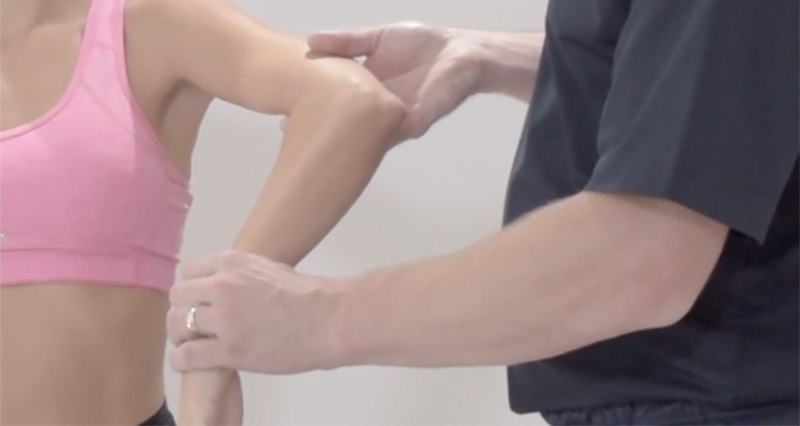
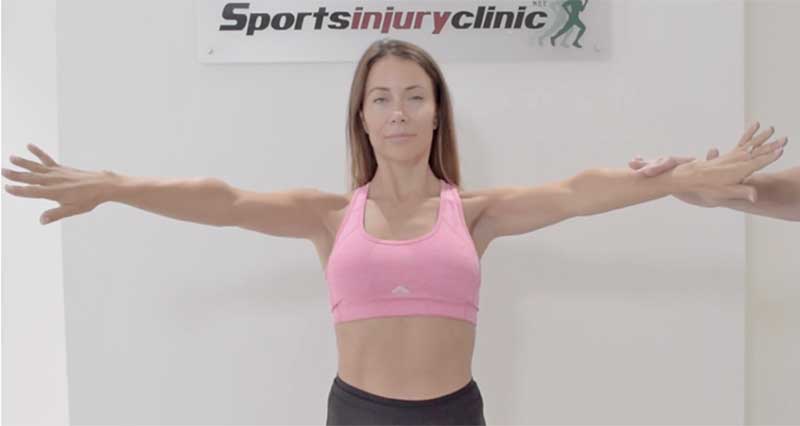
O’Brien’s test, also known as the active compression test, evaluates for labral tears or other pathologies within the shoulder joint, particularly the glenoid labrum.
What is an AC Joint Sprain?
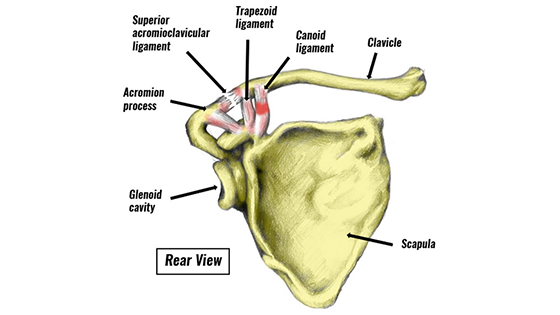
An Acromioclavicular joint sprain (AC) involves tearing or stretching the ligaments that connect the clavicle (collarbone) to the shoulder blade. This injury can vary. For instance, a minor sprain only stretches the main acromioclavicular ligament. However, a severe sprain ruptures multiple ligaments, causing the clavicle to protrude and deform the shoulder.
How to perform the test:
Have the patient stand or sit comfortably facing you. Instruct them to fully flex the shoulder to 90 degrees and bring the arm across the body. Then, have them internally rotate the arm, thumb pointing downward. While they resist, apply downward force on the arm with one hand on the wrist and the other on the elbow for stability. Repeat this with the arm externally rotated, thumb pointing upward.
What is a positive O’Brien’s test?
If internal arm rotation (thumb down) causes pain that external rotation (thumb up) eases, it likely signals a SLAP lesion. Persistent or worsening pain with external rotation could point to AC joint issues or rotator cuff problems.
O’Brien’s test is useful for detecting SLAP lesions. This is a tear at the top of the glenoid socket where the biceps tendon attaches. These tears can cause pain, clicking, or instability in the shoulder during overhead or forceful movements. However, a positive O’Brien’s test alone doesn’t confirm a SLAP lesion; it suggests further evaluation with imaging, like MRI or arthroscopy.
Considerations
Perform O’Brien’s test carefully to avoid worsening the patient’s symptoms. Additionally, it’s crucial to match O’Brien’s test results with other clinical findings, imaging, and patient history for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Overall, healthcare professionals find O’Brien’s test valuable for assessing labral tears, especially SLAP lesions, in patients with shoulder pain or instability.




