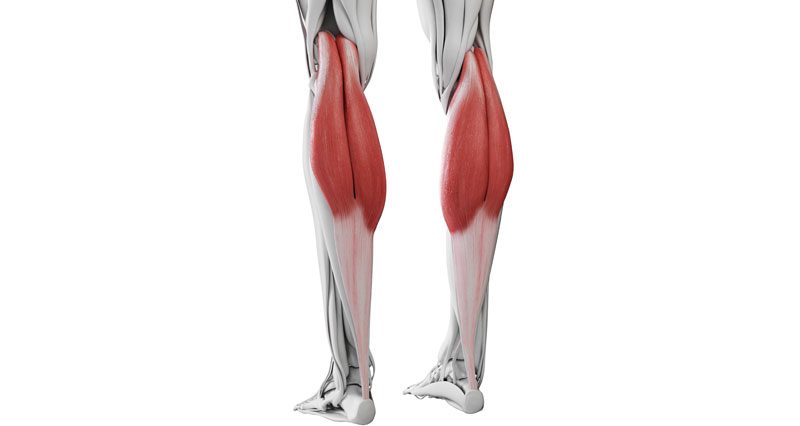
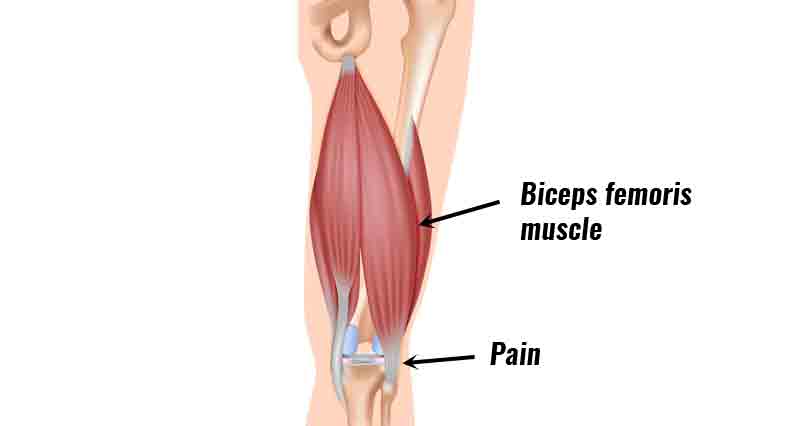
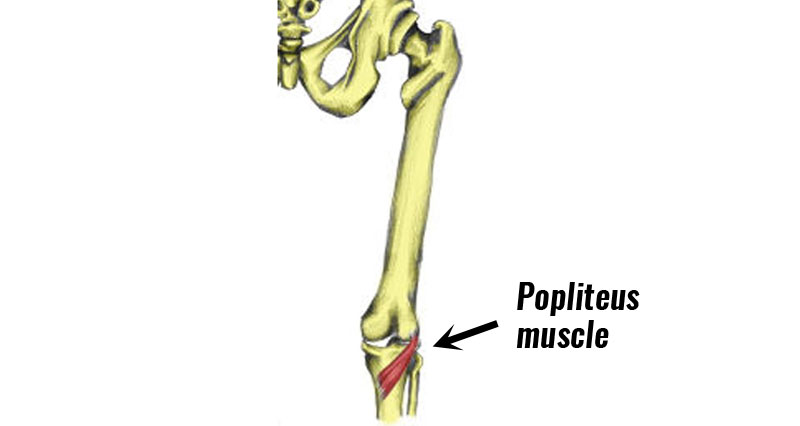
Gastrocnemius tendonitis is inflammation of the gastrocnemius tendon at the back of the knee. It is most likely an overuse injury, more common in runners and sprinters. The gastrocnemius is one of the large muscles at the back of the lower leg which make up the calf muscles.
Symptoms
Symptoms usually develop gradually and include:
- Pain at the back of the knee.
- Tenderness when pressing in behind your knee.
- Pain when performing a straight-leg calf raise exercise.
- Hopping on your injured leg will also be painful.
- Sometimes calf stretching exercises may also be painful, but not always.
Your physio might try to reproduce your symptoms by resisting as you bend your knee (resisted knee flexion).
Buy Knee Braces
What causes Gastrocnemius tendonitis?
Calf tendonitis is an overuse injury. The term tendinitis is often used which indicates inflammation. This is more likely if your injury is recent, or acute.
If your symptoms have developed gradually, or you have been suffering for a number of weeks, then it is possible your injury is more degeneration rather than acute inflammation. Therefore, tendinopathy is often a more appropriate term.
Although overuse is the primary cause, there are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of injury:
- Increasing your running mileage too soon.
- Doing too much high-intensity sprinting.
- If you have a muscle imbalance in your hip or knee joints.
- Poor foot biomechanics. For example overpronation.
- Wearing incorrect or poorly fitting footwear should also be considered.
Treatment for Gastrocnemius Tendonitis
Initial treatment consists of applying the PRICE principles of protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Rest
Rest is important to protect from further damage and allow the injury to heal. In minor cases, this may just initially consist of modifying training. For example, avoiding sprinting if it hurts to run fast, or avoiding running altogether in favour of cycling or similar.
Cold therapy
Ice helps to reduce pain and inflammation and is very important in the early stages (48 to 72 hours). Once your initial pain and inflammation have gone, you can begin a gradual stretching and strengthening program. This ensures your injury does not recur when you return to normal training loads.
Knee supports
Wear knee support or a heat retainer. This supports and protects your knee. A neoprene-type brace retains your body’s heat, stimulating blood flow. As a result, the healing process is helped.

Buy Kinesiology Tape
What can a sports injury professional do?
- A professional therapist can make an accurate diagnosis and may use electrotherapy such as ultrasound to help reduce pain and inflammation.
- A doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication such as Ibuprofen in the early stages to help reduce pain and inflammation, although long-term use is not thought to aid the healing process.
Massage
Sports massage to the calf muscles is important to help relax and stretch the muscle which will reduce the strain on the tendon and enable the muscle to function better during activity. Local cross-friction massage to the tendon itself may be used in more chronic cases.

Foam Rollers
Exercises for Gastrocnemius Tendonitis
- Stretching exercises for the calf muscle in particular and the hamstring muscle should be done as soon as pain allows and maintained throughout the rehabilitation process and beyond.
Go to calf stretching exercises.
- Strengthening exercises for the calf muscles can also begin after the acute stage as long as they can be done pain-free.
- For more severe injuries this may start with simple plantar flexion exercises with a resistance band and progress to calf raise exercises on a step.
- Begin with both legs and as strength and confidence improve this can be developed into single-leg calf raises.
Go to calf strengthening exercises.