Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction or PTTD is a dysfunction of the posterior tibialis muscle, resulting in a fallen arch, or flat feet. The tibialis posterior tendon supports the arch of the foot so if it becomes impaired, or is not working properly the arch of the foot collapses.
Symptoms of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
Symptoms of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction vary depending on the extent of the condition. In other words, how far it has progressed.
Early stage symptoms
- Pain on the inside of the ankle and/or under the foot.
- Your foot arch begins to flatten.
- Redness and swelling.
- You may have a history of injury to the tibialis posterior muscle.
Later stage symptoms
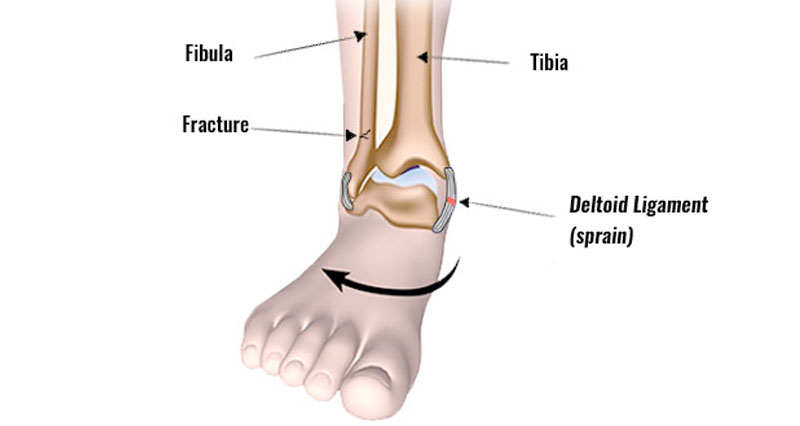
As the condition progresses your arch flattens more and rotates outwards. Your ankle rolls inwards. Eventually, as your foot collapses, pain is more likely on the outside of the foot. Arthritis may develop in the foot.
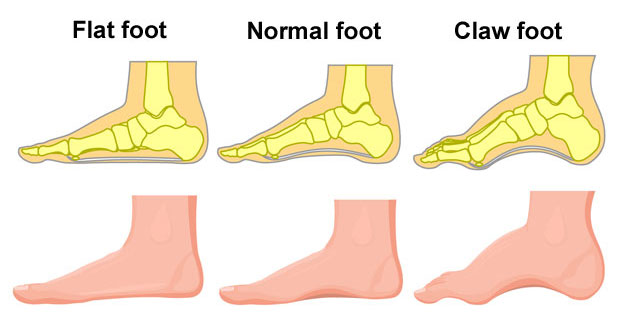
What is Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
Posterior tibial syndrome is a dysfunction of the muscle, resulting in a fallen arch, or flat feet.
The following terms are all used:
- Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD)
- Posterior tibial tendon syndrome
- Tibialis posterior syndrome
- Posterior tibial insufficiency
- Adult acquired flatfoot
All of these conditions are the same and so we will interchange them in this article.

Technical Running Socks
There is also confusion between this condition and tibialis posterior tendinopathy. They are not the same. The latter is a degenerative, painful injury to the tendon of the tibialis posterior.
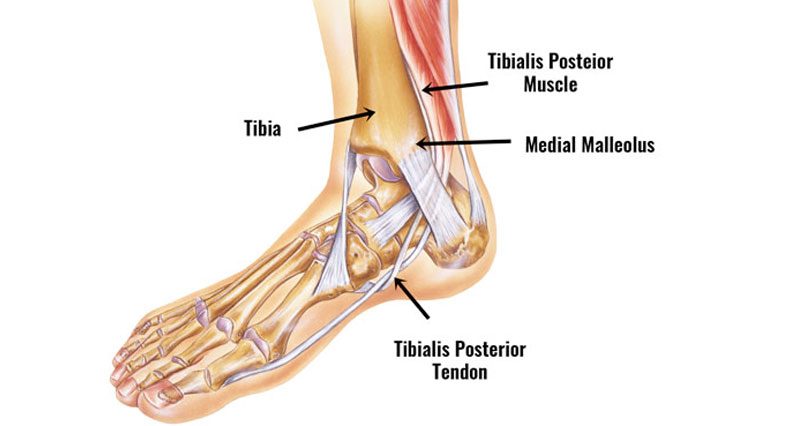
Anatomy
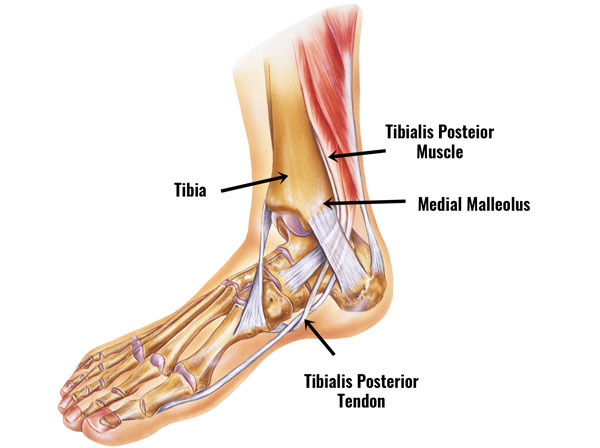
The tibialis posterior muscle originates from behind the shin bone or tibia and runs into a tendon that passes behind the bony bit on the inside of the ankle (medial malleolus).
Its function is to plantarflex the ankle (point the foot down) and invert the foot (turn the sole inwards).
What causes PTTD?
A common cause of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is overuse. For instance, long-distance road running and walking. As a result, repetitive strain gradually weakens the muscle.
Because the Tibialis Posterior muscle is responsible for inverting the foot, if it is not working correctly, then this causes the arch of the foot to flatten when we stand, walk or run. The fallen arch or flat feet can then cause further injury problems such as plantar fasciitis.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction treatment
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a progressive condition. This means it becomes gradually worse. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are important. If caught early enough, conservative treatment (without surgery) should be sufficient.
Treatment of any associated conditions such as tibialis posterior tendinopathy is also important.
Cold therapy
If your injury is painful or acute, then rest and apply ice or cold therapy. This reduces pain, inflammation, and swelling.
Correcting biomechanical dysfunction
A professional therapist such as a Podiatrist can do a full assessment including gait analysis to identify problems such as overpronation.
They may prescribe arch support insoles or orthotic insoles to help correct biomechanical problems of the foot.
PTTD braces
Specialist PTTD braces or ankle supports can help take the strain off the tibialis posterior muscle whilst it is healing. They can help prevent PTTD from progressing or help with recovery after surgery.
Sports massage
Deep tissue massage to the muscles at the back of the lower, particularly the tibialis posterior muscle can help relax the muscle and remove, and tight knots, lumps, and bumps.

Foam Rollers
These are areas where the muscle has tightened up or gone into spasm, and therefore unable to work optimally.
Getting a regular sports massage can help identify potential muscle injuries before they become full-blown injuries.
Exercises for PTTD
Exercises to strengthen the tibialis posterior muscle are an important part of treatment and rehabilitation. This is done in a similar way as strengthening the calf muscles with plantar flexion-type exercises but with inversion of the ankle as well.
Tibialis posterior strengthening
Begin with strengthening exercises using a resistance band and as pain allows and strength improves move on to calf raise-type exercises.
The Tibialis Posterior muscle works to both invert and plantarflexes the foot ankle.
Inversion using a step
This exercise is a more advanced tibialis posterior muscle strengthening exercise, using body weight as resistance.
Teaching point:
- Stand (in bare feet) long ways on a step with the inside of the foot halfway over the step.
- Gently roll the foot inwards (evert or pronate) so the inside of the foot rolls in and downwards.
- Return to the starting position by inverting it so it is flat on the step again.
- Aim for 3 sets of 10 repetitions and gradually build up to 3 sets of 30 repetitions.