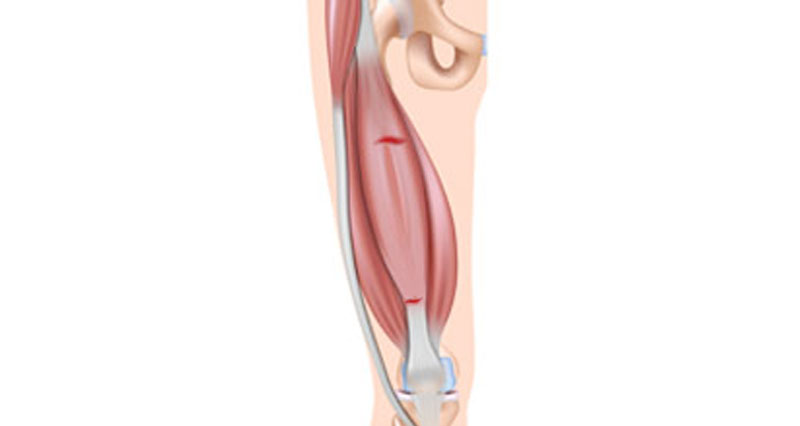
A thigh strain is a tear to one of the quadriceps muscles at the front of the thigh. Thigh strains are graded 1, 2 or 3 depending on how bad they are. Here we explain thigh strain diagnosis and how to tell what grade of injury you have.
Medically reviewed by Dr. Chaminda Goonetilleke, 21st Feb. 2022
How bad is my thigh strain?
A thigh strain (quadriceps muscle tear) causes sudden acute pain at the front of the thigh. Muscle strains are graded 1 to 3 depending on how bad they are an how much of the muscle has torn.
Grade 1
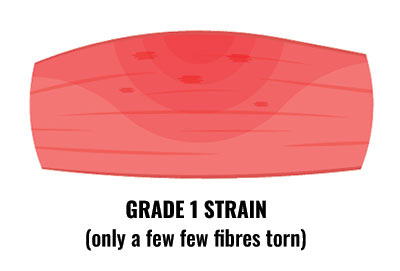
- If you have a grade 1 quad strain then it may not feel bad enough to stop training at the time.
- You might feel a twinge in the thigh, with a general feeling of tightness.
- Walking may cause mild discomfort and running might be difficult.
- You are unlikely to have swelling, but you may feel a lump in the muscle.
Grade 2
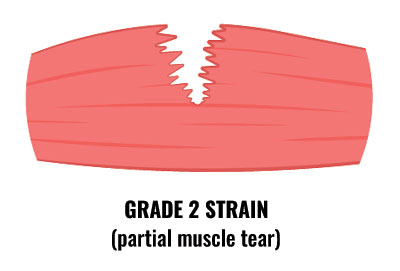
- Grade 2 symptoms are more severe than grade two.
- You may feel a sudden sharp pain when running, jumping or kicking and be unable to play on.
- Pain will make walking difficult and you will notice swelling or mild bruising.
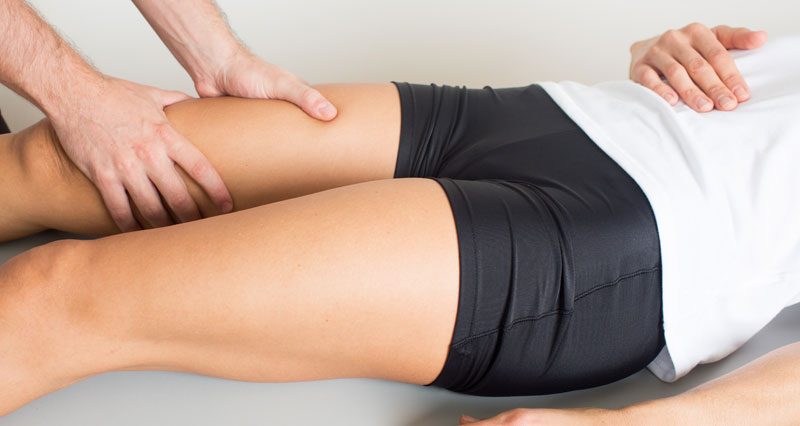
- The pain would be felt when pressing into the muscle, particularly where it is torn.
- When diagnosing thigh strains your therapist will get you to straighten your leg whilst they resist it. Pain indicates injury to the muscle.
Grade 3
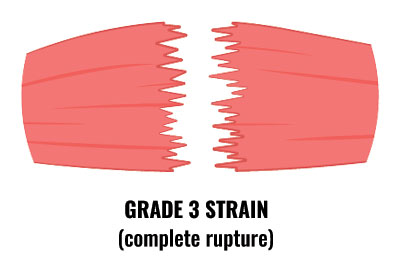
- Grade 3 symptoms consist of severe, sudden pain in the front of the thigh.
- The patient will be unable to walk without the aid of crutches.
- With grade 3 thigh strains, significant swelling can develop immediately. Bruising deveops within 24 hours.
- A static muscle contraction will be painful and is likely to produce a bulge in the muscle.
- The patient can expect to be out of competition for 6 to 12 weeks.
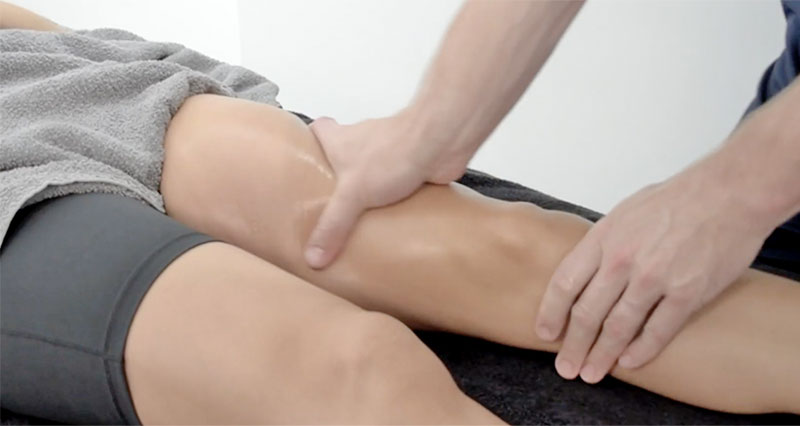
Thigh strain assessment & diagnosis
A professional therapist will do a full assessment in order to accurately diagnose your injury. This should include:
- Questions about your general health, previous injury as well as current injury.
- Your therapist will then perform a physical assessment of the injury.
- This includes observation and palpation (feeling the area),
range of motion tests and resisted muscle tests.