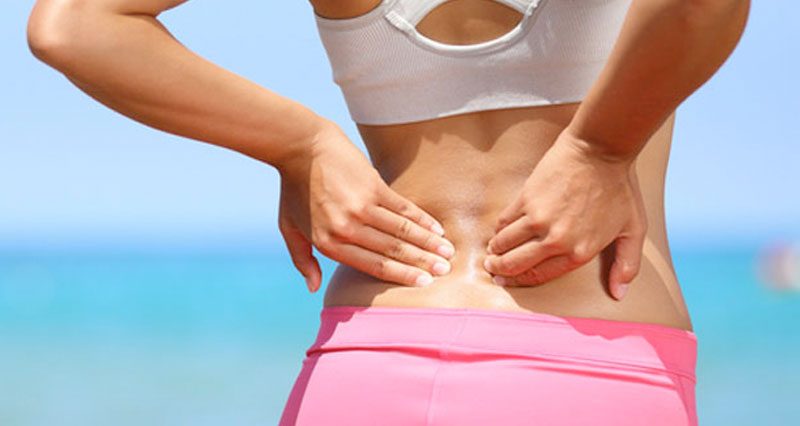
Acute low back pain is a severely painful back pain that usually comes on suddenly from a movement such as bending over or twisting. It often results from a chronic or long-term back injury which flares up worse from time to time.
Acute back pain
Diagnosing the exact cause of acute back pain is often difficult. It is possible to injure a number of structures in the back. Identifying whether it is a ligament, tendon, muscle strain or something else can be complex. The important thing initially is to treat the symptoms and seek professional medical advice.
The initial treatment of acute low back pain is to make the patient as comfortable as possible and reduce pain and inflammation as quickly as possible. Below we outline some simple steps to help relieve acute low back pain.
Treatment for acute low back pain
The first thing to do is get into a position of most comfort. This could be lying on the back, on the side, or front. Whatever is least painful is best and may be different for each individual. Some people may find keeping moving gives the most pain relief. The psoas position lying on the back with the knees bent and up on a chair can often be the best position.
Avoid any movements or activities which make the pain worse. Bed rest may help but not for more than two days as resting for too long can make back injuries worse. Often movement is needed after the initial pain and inflammation have gone.
If a muscle strain or ligament sprain is suspected and there is any swelling or bruising then applying a cold pack can help reduce painful symptoms and swelling. Never apply ice directly to the skin as ice burns can occur. Cold should be applied for 10 minutes every hour initially and reduced as required. If symptoms get worse with cold therapy then discontinue. Later on, when the initial bleeding has stopped applying heat or alternating hot and cold may be more beneficial. This is usually after the first 24 to 48 hours.
Using a back support or back brace can provide some relief from back pain as can sports taping or kinesiology taping. A back support will compress the muscles and other structures in the lower back taking some of the stress off them and relieving pain, particularly if the patient is required to stand. A doctor may prescribe pain-killing medication or NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) to relieve pain and muscle spasms. Always check with a doctor before taking medication as some medicines such as Ibuprofen should not be taken if you have asthma.

Buy Back Supports
Electrotherapy
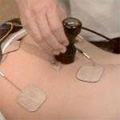
Electrotherapy such as electrical stimulation (TENS), Ultrasound therapy, or magnetic field therapy may be useful in relieving back pain symptoms.
Tens or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation passes electrical signals into the muscles which can block pain signals to the brain and stimulate the muscles into a movement that may also relieve symptoms.
Ultrasound therapy passes high-frequency sound waves into the tissues providing a micro-massage and painkilling effect, also relieving spasms in the muscles.
Massage
Light massage techniques may help reduce pain, particularly if muscles have gone into spasm. Massage will help flush tissue fluids and blood through the muscle, warming them and reducing, and painful muscle tension which may be contributing to back pain.
Inversion
The use of an inversion table may help relieve symptoms. The patient lies on a board and is partially or fully inverted allowing gravity to apply gentle traction to the spine releasing pressure on the tissues and structures of the lower back.
Posture
Avoid sitting for long periods of time. This can cause muscles to go into spasms as they are not used and blood does not flow through them so easily. Adaptive shortening of muscles can also cause posture problems long-term.
A full rehabilitation program consisting of back exercises for mobility and strength should be started as soon as possible to avoid any muscle wasting and long-term consequences of the back injury. See a sports injury or back pain specialist who can advise on treatment and rehabilitation. If any back exercises are painful they should be discontinued.

Zinc Ocide Sports Tape
Mobility exercises
The following guidelines are for information purposes only. We recommend seeking professional advice before beginning rehabilitation.
Lower back stretch
- Lie on your back.
- Pull knees up to chest as far as they will go.
- Hold for 10+ seconds, repeat 5 times.
- This exercise stretches the muscles around the lumbar vertebrae.
Side stretch
- Standing upright, lift one arm above your head.
- Lean over to one side as far as is comfortable.
- Hold for 10-20 seconds.
Pulling knee up
- Lie on your back with both legs out straight.
- Raise one knee gently up to the chest and bring the head up to meet it.
- Lower the knee back down and repeat with the other leg.
- Repeat the exercise 10 times on each leg.
Cat stretch
- Start on your hands and knees.
- Arch your back upwards, like an angry cat, hold for a couple of seconds and then arch the back downwards, like a happy cat.
- Repeat this exercise 10 to 20 times.
Knee rolling
- Lie on your back as above with the knees bent.
- Slowly lower both knees to the left whilst turning the head to the right.
- Bring the knees up again and to the right whilst looking left.
- Repeat this movement 10 times.
The above exercises can be performed as soon as pain will allow – usually 48 hours following injury. If any of the exercises hurt then do not continue and seek professional advice. Exercises should be performed at least every day, two or even three times a day if possible, especially in the first two weeks of rehabilitation. These exercises should continue long after the injury has healed to prevent it from reoccurring.

Foam Rollers
Back massage
Basic sports massage techniques for the lower back can help relax the muscles and improve their overall condition following a muscle strain but should be avoided in the early stages of acute back pain, especially when tissue damage is suspected.