Headaches are an extremely common complaint. They vary in pain intensity, pattern, and location from individual to individual. Although irritating the majority of headaches do not require medical intervention.
When to seek medical advice
Seek medical attention for a headache if it is new and unaccustomed. Or if you have regular headaches but have changed in their pattern, intensity, or frequency. Also, if your symptoms include:
- Drowsiness
- Numbness
- Stiff neck
- Weight loss
- Fever
Assessment of headaches in sport
Your doctor or physio determines what might be causing your headache, or what type it is. They take a clinical history of symptoms, specifically the location, severity, and frequency of headaches. Also, they need to know:
- Any medication you take
- What aggravates or eases symptoms
- Whether you have other symptoms such as nausea or vomiting
There are a number of different classifications of headaches. Below is an overview of the most common types and those associated with sports.
Vascular headaches
These headaches are extremely common, affecting approximately 20% of the population at some stage of their life. We think an increase in blood flow to the head causes the throbbing sensation often experienced.
Two main types exist:
Migraine
Signs and Symptoms of a migraine:
- Intense, throbbing, or pounding felt periodically in the forehead, temple, ear, jaw, or around the eye
- Prior to the pain, patients may see flashing lights, stars, or other white objects
- Visual disturbance
- Problems with speech
- Vomiting and nausea
A number of factors predispose some people to migraines:
Read more on Migraines
Cluster Headache
These headaches are so-called as they commonly occur in ‘clusters’ over a period of weeks or months, at approximately the same time of day.
Signs and Symptoms of a cluster headache:
- Intense pain
- A burning or boring sensation often immobilising the patient
- Cluster headaches are about 5 times more common in men
- Attacks may last from 30-45 minutes
Treatment for a cluster headache:
Specific anti-migraine drugs can help with the symptoms of a cluster headache. Also, rapidly inhaling pure oxygen through a mask for 5 to 15 minutes. Although, the mechanism for this is unclear.
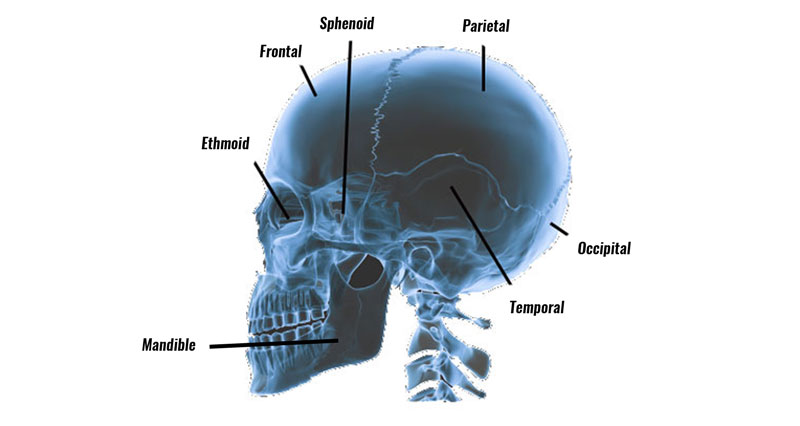
Cervical headache
The other main type of headache is a cervical headache. These headaches are caused as a result of dysfunction in the muscles, joints, nerves, or fascia in and around the neck region. Pain radiates towards the skull giving the sensation of a steady dull, ache.
Causes of a cervical headache
- Nerve compression in between the neck bones
- Abnormal tenderness in the neck tissues is associated with trigger points in certain muscles.
- Limited neck range of movement i.e. ‘stiff neck‘
Treatment of a cervical headache
- Massage to release tension in the muscles
- Acupuncture
- Posture retraining is similar to that which might be done for someone with Kyphosis of the neck.
Exercise-related headaches
A number of headaches can be sustained as a result of sports:
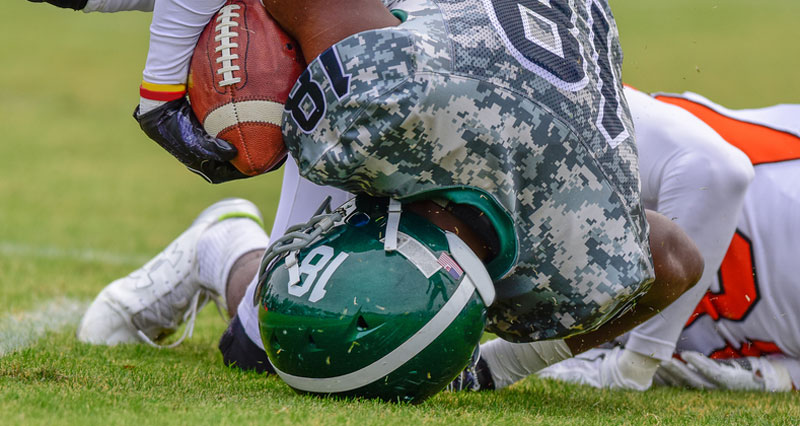
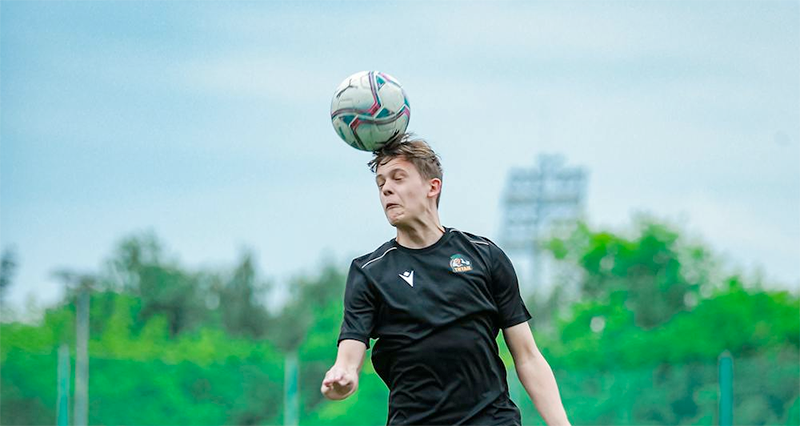
‘Footballers Migraine’ (Post-traumatic Migraine)
- This is caused by trauma to the head which may be as small as heading the ball rather than a full-on collision resulting in a more serious concussion injury.
- May result in loss of consciousness.
- Tends to resolve itself in a few hours.
‘Swim Goggle Headache’ (External Compression Headache)
- Caused by compression on the skull, for example, by a swimming goggle strap.
- Compression is thought to stimulate the nerves under the skin causing pain in the head region.
‘Divers Headache’ (Hypercapnia Headache)
- Thought to be caused by an increase in the pressure below a certain depth. This may lead to an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.
‘High Altitude’ A headache:
- Usually occurs in an unacclimatized person shortly after ascending to an altitude of about 4000 to 6000 feet.
- May be associated with mountain sickness.
‘Benign Exertional’ A headache (BEH)
- Common in weightlifting and other sports where over-exertion occurs.
- During exertion, blood pressure increases causing more blood to flow to the head. In certain cases, this may manifest as a throbbing pain.
- May last from a few minutes to 24 hours.