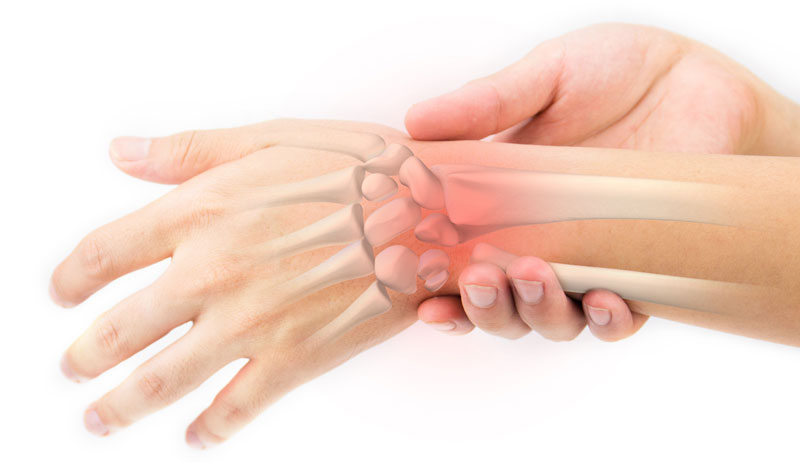
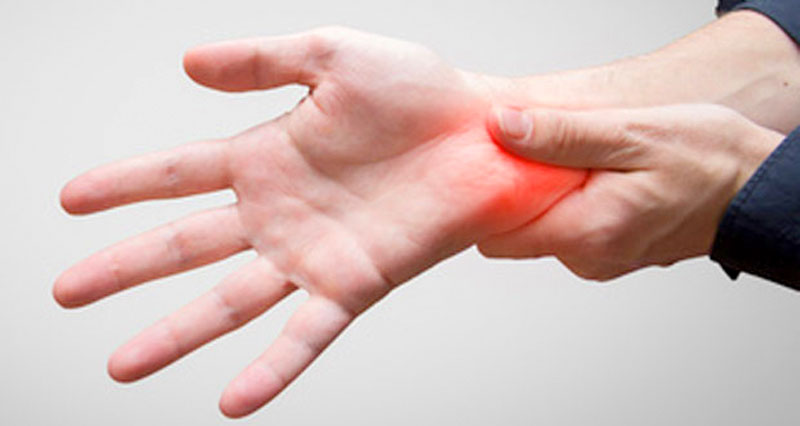
Here we explain the causes of sudden onset or acute wrist pain including sprains, strains and fractures.
Wrist sprains & strains
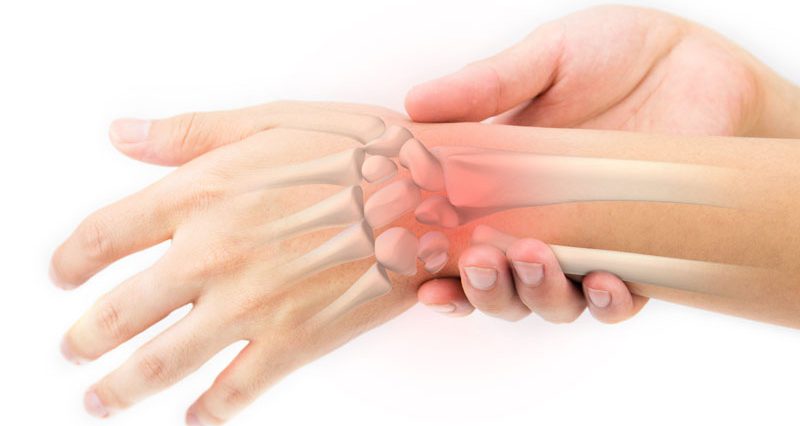
A sprain is a tear of a ligament which joints bone to bone. A strain is a tear of a tendon which joins muscle to bone. They can occur at the same time.
Wrist sprain
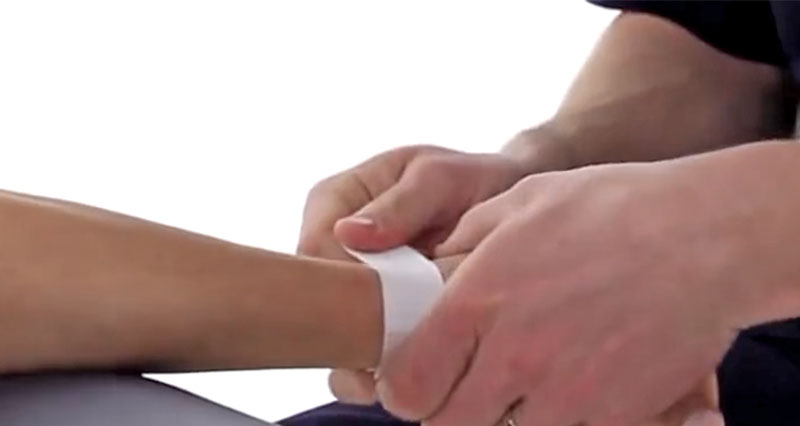
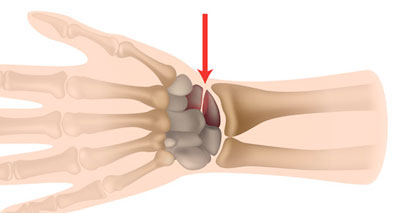
A sprained wrist is an injury to any of the ligaments which connect bone to bone in the wrist. Wrist sprains are usually caused by trauma such as falling onto an outstretched arm.
- Symptoms vary depending on the extent and the location of the sprain.
- Sudden pain in the wrist will be felt at the time of injury.
- In severe sprains, a tearing or popping feeling may be felt.
- A particularly tender spot may be felt where the ligament is damaged.
- Swelling could be visible and bruising might develop in more severe injuries.
- More on wrist sprain
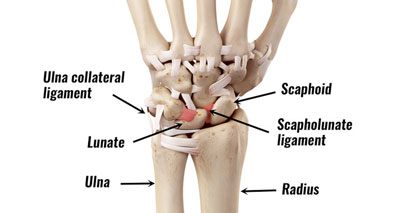
TFCC tear
A TFCC tear is an acute injury to the triangular fibrocartilage complex, found in the wrist, between the end of the ulna bone and the carpals.
A tear can be caused by a specific incident or come on gradually, resulting in wrist pain and restricted wrist and hand function. This wrist injury can often be treated with a splint, although if it is too severe, surgery may be needed.
- More on TFCC tears
Wrist strain
A wrist strain is a tear of any of the tendons in the wrist. It usually occurs suddenly (acute injury), or can develop over time through repetitive stress and overuse (chronic wrist pain). Symptoms of a wrist strain include:
- Pain in the wrist which may develop gradually or suddenly.
- There may be a specific area which feels tender to touch.
- Swelling may develop, but not always.
- More on Wrist strain
Fractures
Have I broken my wrist? There are many different types of wrist fractures. Symptoms will be sudden onset pain, swelling, restricted movement.
If you are in any doubt about whether you have a fractured wrist then seek medical advice immediately.
Distal radius fracture (Colles fracture)
A Colles fracture is a particular type of broken wrist that involves a break of the radius or forearm bone on the thumb side of the wrist. Symptoms which would indicated a fracture consit of:
- Severe pain
- Deformity
- Rapid swelling would indicate a fractured wrist.
- More on wrist fractures
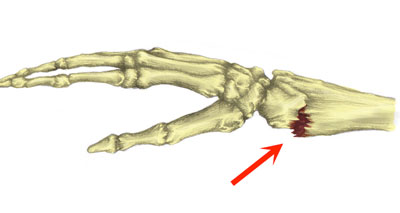
Scaphoid fracture
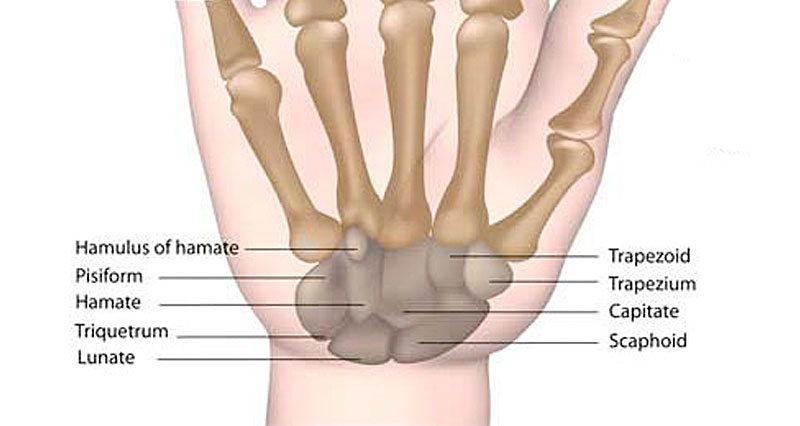
The scaphoid is one of the small group of bones in the wrist called the carpal bones. It is the most common carpal bone to fracture among athletes and is often caused by falling onto an outstretched hand. Wrist pain and trouble gripping things are symptoms of this type of fracture, and medical advice should be sought for treatment.
Symptoms of a scaphoid fracture include pain in the wrist at the time of injury and rapid swelling at the back of the wrist. Pain may settle down soon after the fall but the patient will have difficulty gripping things. There will be tenderness when pressing in on the wrist compared with the noninjured wrist.
- More on wrist fractures
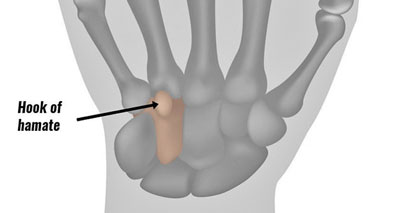
Hook of hamate fracture
The wrist contains a number of small bones called carpals. The hamate is a carpal bone on the outside (little finger side) of the wrist.
It has a hook-shaped part which protrudes outwards and can under certain circumstances be fractured. With this injury, wrist pain occurs on the side of the little finger and the strength of grip can be reduced.
- More on wrist fractures
Distal radial epiphysis injury
A distal radial epiphysis injury is an acute injury to the growth plate at the wrist end of the radius (forearm) bone. It mostly affects children and young athletes, particularly gymnasts, between the ages of 6 and 10 years old. Overuse is the most likely cause.
- Symptoms include acute pain in the wrist, especially when the wrist is bent backward with the palm facing down (known as dorsiflexion).
- They are likely to have limited movement in the wrist, which can prevent gymnasts from performing certain movements.
- There may be tenderness and swelling around the end of the bone.
- Other injuries with similar symptoms include ganglion cysts, wrist tendonitis.
- More on Distal radial epiphysis Injury
Distal radioulnar joint instability
The distal radioulnar joint is the joint at the wrist, between the radius and the ulna, the two forearm bones. This injury is usually a subluxation, or a partial dislocation, although fractures of either bone can be involved.
It is often caused by a direct impact like a fall, and medical help is needed immediately to check and treat the wrist injury.
Dislocated wrist
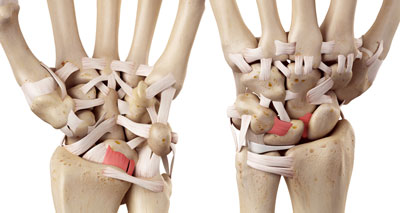
This is thankfully a rare but traumatic cause of acute wrist pain. A dislocated wrist is a dislocation of any of the eight small bones called carpal bones which make up the wrist. A wrist dislocation will occur as a result of a traumatic event or a fall onto the wrist. There is usually an obvious deformity along with acute wrist pain when dislocation occurs. Medical help is needed immediately, particularly as the ligaments and nerves can be seriously damaged.
- Symptoms usually include severe pain with an obvious deformity in the wrist.
- Tingling may develop in the thumb, index, and middle fingers which suggests associated median nerve damage.
- Medical attention should be sought immediately if a dislocation is suspected.
The eight carpal bones in the wrist are the hamate, capitate, pisiform, trapezoid, trapezium, scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum. There are a number of ways in which the carpal bones dislocate and the lunate bone is usually involved in most of them. A dislocation of the carpal bones will involve severe ligament damage and if left untreated can result in permanent disability. Two significant dislocations are anterior (front) dislocation of the lunate and perilunar dislocation of the lunate.
Treatment for a dislocated wrist: Carpal dislocations usually require surgical treatment by a specialist wrist and hand surgeon. He or she will put the bones back in place and repair any ligament and soft tissue damage. The wrist is then immobilized in a cast for 8 weeks to allow time for the injury to heal.
Once out of the plaster cast a full rehabilitation program with wrist strengthening exercises should be done to restore the hand and wrist to full normal functioning and help prevent any future injury.