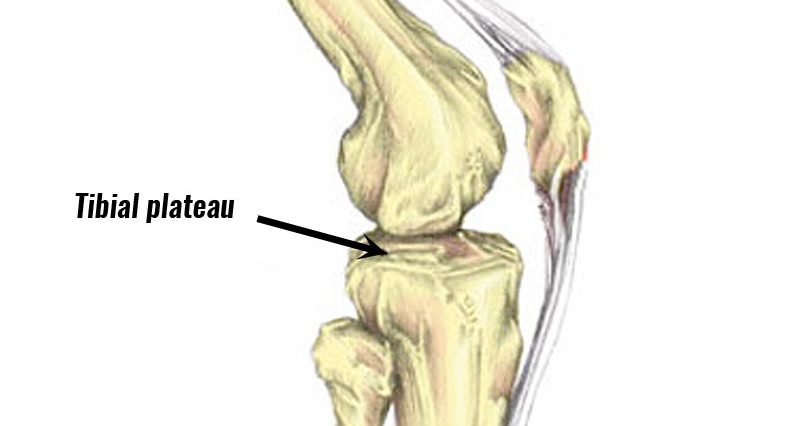
A tibial plateau fracture is a break to the upper surface of the tibia (shin bone). The tibial plateau is prone to becoming fractured in high-speed accidents such as those associated with skiing, horse riding, and certain water sports.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 14th Dec. 2021
Tibial plateau fracture symptoms
- There is normally a recent history of trauma to the knee.
- Severe pain and swelling in the knee joint.
- You will be unable to weight bear and may complain of the stiffness of the knee joint.
Imaging
In order to correctly diagnose a fracture, an X-ray must be performed although a CT scan is frequently required for surgical planning.
What is a tibial plateau fracture?
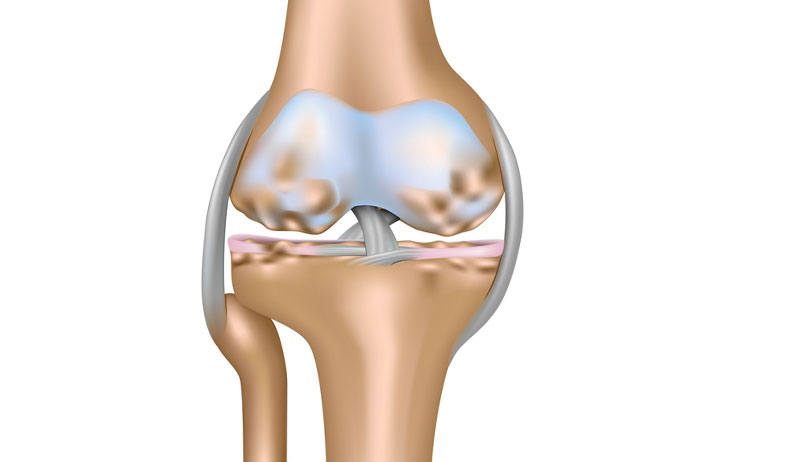
A Tibial plateau fracture is a fracture of the upper surface of the tibia bone.
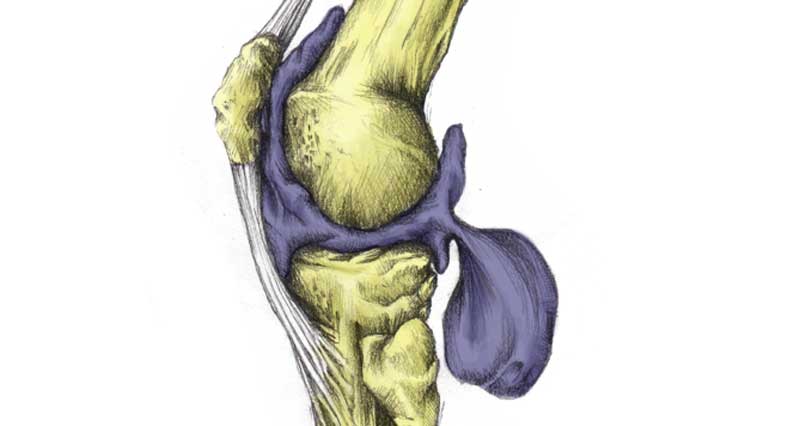
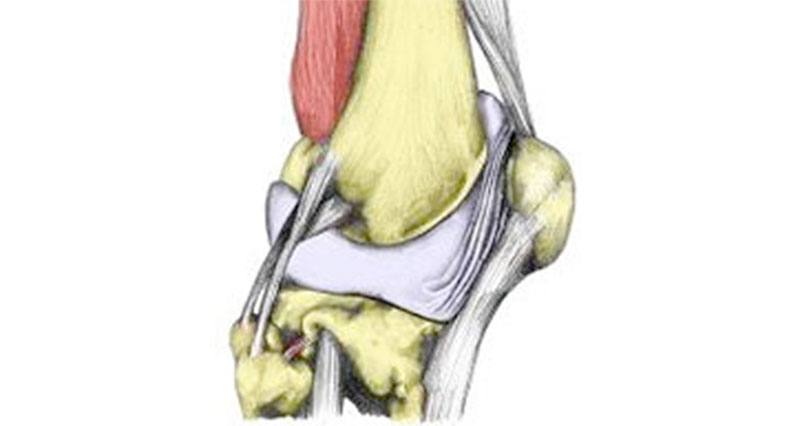
It is quite a serious injury. The upper surface of the tibia bone contains structures that are critical to the knee’s functioning. In particular, the cartilage meniscus and the cruciate ligaments attach there. They are essential for a stable knee.
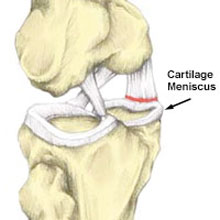
Therefore, tibial plateau fractures often occur in conjunction with injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, collateral ligaments (MCL or LCL), menisci, and articular cartilage. This damage, although repairable, makes you much more susceptible to the early onset of osteoarthritis, particularly in younger patients.
Treatment
Rest and apply cold therapy or ice and compression to help reduce pain and swelling. Seek medical assistance immediately.
Once your tibial plateau fracture has been diagnosed a number of treatment options are available depending on the extent of the damage.
How bad is my injury?
In surgical terms, there are 6 different classifications, depending on the severity and the nature of the injury. However, the two main groups are:
- Displaced fractures
- Non-displaced fractures
Non displaced tibial plateau fracture
A non-displaced fracture is when the tibia sustains a break or crack without a fragment of the bone becoming separated.
These normally have a better outcome than displaced fractures and heal without surgical intervention within 3-4 months.
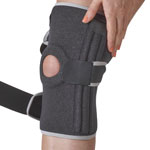
During this time the patient should not weight bear. They should wear a knee brace to protect the knee.
Maintain leg strength with rehabilitation exercises as soon as possible after injury. Continue building strength throughout the recovery phases.
Displaced tibial plateau fracture
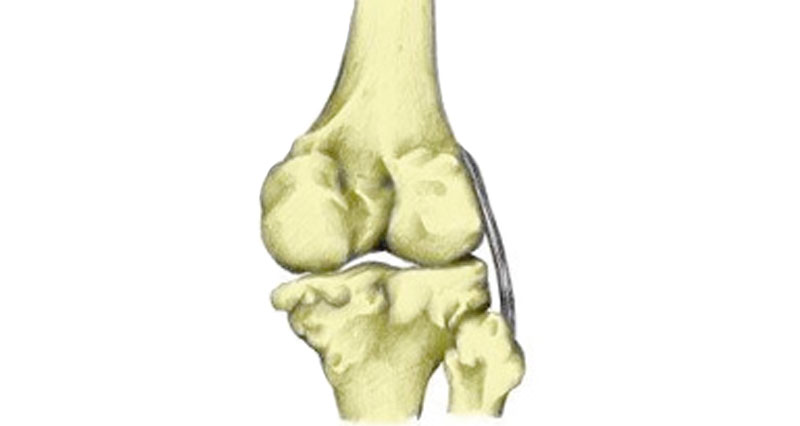
A displaced fracture is one where the bone breaks into two or more fragments. If this happens then you will most likely need surgery to fix the fragments in place. This encourages correct healing of the bone tissue.
This fixation is usually achieved by placing screws and/or plates in and around the bone fragments to keep them secure.
In situations where there was an open fracture (where bony fragments were exposed), a ring-like metal brace called an external fixator may be used.
Recovery following surgery may take a number of months and will require the patient not to weight bear for a long period of time. If soft tissue injuries have been sustained this recovery process may take longer.
References & further reading
- Google Scholar – Tibial plateau fracture