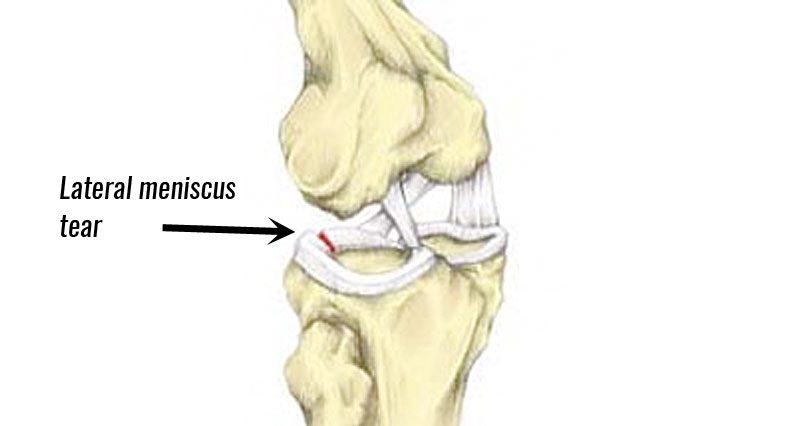
A lateral meniscus tear is an injury to the semi-circular cartilage resulting in pain on the outside of the knee joint. It can occur suddenly from twisting or a traumatic collision. Or it may develop gradually through wear and tear or overuse.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 10th Dec. 2021
Lateral knee meniscus tear symptoms
Symptoms of a lateral meniscus tear will vary depending on whether your injury is an acute, sudden onset injury resulting from direct impact, trauma, or twisting. Or whether your pain has developed gradually over time through wear and tear.
Acute symptoms
Acute meniscus tears occur suddenly. You will know a specific time when your injury occurred. Symptoms are:
- Sudden pain at the time of injury.
- The outside surface of your knee will feel tender when pressing in, particularly along the joint line.
- Your knee is likely to swell up either immediately, or within 24 to 48 hours.
Chronic symptoms
Chronic meniscus injuries develop gradually over time. You will be unlikely to pinpoint precisely when your injury occurred. In children particularly, meniscus tears may be difficult to diagnose as pain may be vague and difficult to pinpoint. Symptoms may include:
- Swelling, pain, and tenderness along the joint line on the outside of your knee.
- Pain when bending your knee or squatting.
- You may experience a snapping or clicking sound when bending your knee.
- Your knee may also lock.
Buy Knee Braces
Diagnosis
Your doctor or physio will perform a full knee assessment. This includes specific assessment tests to confirm the diagnosis. For example, McMurray’s test and Apley’s test.
McMurray’s test
McMurray’s test is often used to indicate cartilage injuries. With the patient laying on their back the therapist holds the knee with the upper hand and the heel with the lower hand. The therapist then applies a valgus (inward) stress to the knee whilst the other hand rotates the leg externally (outwards) and extends the knee. Pain and/or an audible click while performing this manoeuvre can indicate a torn medial meniscus.
Apley’s test
Apley’s test is also used in cases of suspected meniscus tears. The patient is positioned on their front with the knee bent. The therapist grasps the heel and ankle and applies a compressive force through the lower leg. At the same time, they rotate the lower leg. Any reproduction of symptoms, pain, or clicking is a positive response, suggesting a torn meniscus.

Buy Knee Braces
Imaging
An MRI scan may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and extent of the injury.
What is a Lateral meniscus tear?
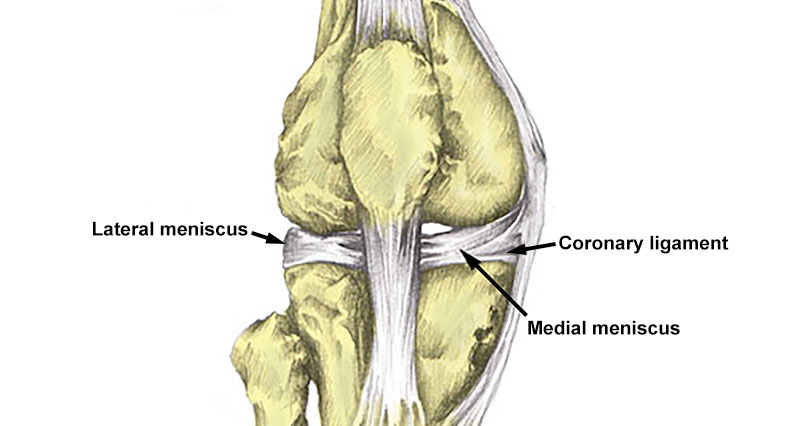
A lateral meniscus tear (torn meniscus) is a tear of the semicircular fibrous cartilage discs in the knee.
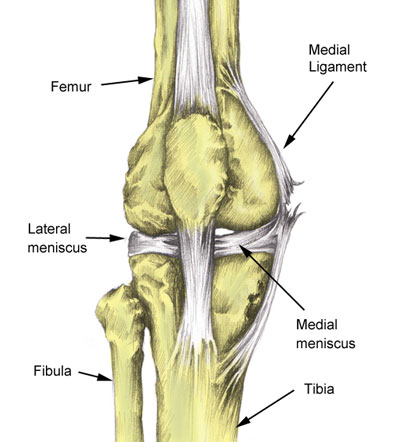
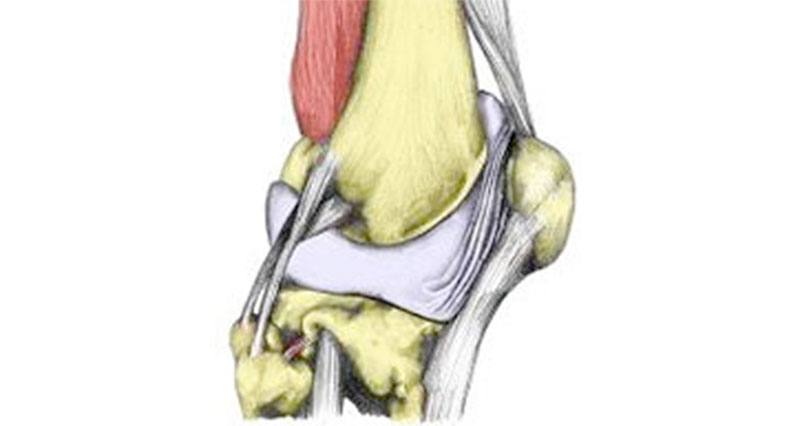
Each knee joint has two crescent-shaped cartilage menisci. These lie on the inside (medial) and outside (lateral) edges of the top of your tibia (shin bone). This part of the tibia is also known as the tibial plateau.
The menisci (plural of meniscus) act as shock absorbers for the knee. They also provide support and stability for the knee joint. Injuries to either the medial meniscus or lateral meniscus can prevent your knee from functioning properly.
The lateral meniscus is less prone to injury than the medial meniscus. This is because it doesn’t attach to the lateral knee ligament in the same way that the medial cartilage meniscus attaches to the medial ligament. A tear of the lateral meniscus can occur during twisting movements, direct impact to the knee joint, deep squats, or due to degeneration of the cartilage, particularly in older athletes.
Types of meniscus injury
There are different types of meniscus tears:
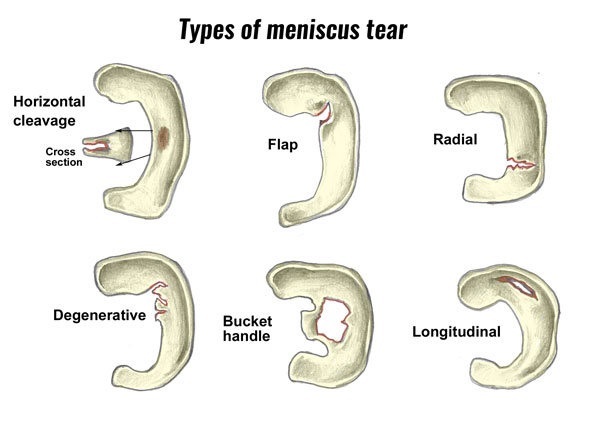
Degenerative Changes may lead to the edges of the menisci becoming frayed and jagged.
A longitudinal meniscus tear is one that occurs along the length of the meniscus.
A bucket handle meniscus tear is an exaggerated form of a longitudinal tear. Here a portion of the meniscus becomes detached from the tibia. As a result, a flap that looks like a bucket handle is formed.
Expert interview
Sports Physiotherapist Neal Reynolds explains torn cartilage meniscus:
Lateral meniscus tear treatment
Treatment for a lateral meniscus tear is usually conservative, to begin with. This means without surgery and consists of a period of rest with rehabilitation & strengthening exercises.
Cold therapy
If your knee is swollen the PRICE principles should be applied (protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Ice can be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 hours initially. You can reduce the frequency as your symptoms improve.
Knee supports/braces
Wear knee support to help protect your knee joint while it heals. A stabilized knee brace has additional springs down the sides to give your knee extra support.
If you have a particularly severe injury then a full-hinged knee brace may be more appropriate.

Buy Knee Braces
Rehabilitation exercises
Gentle exercises to maintain quadriceps muscle strength can be done. However, take care not to aggravate your injured knee.
Once the pain has subsided, the therapist will advise on mobility exercises to increase the range of movement at the knee joint (if needed), along with strengthening, proprioception, and functional or sports-specific exercises should be done.
Seek professional medical advice as surgery may be indicated, especially in active sports people, or if your knee locks or gives way.
Lateral meniscus tear surgery
If the conservative approach doesn’t work then your doctor may recommend surgery. Orthopedic Surgeon Mr Richard Villar explains knee cartilage surgery below:
If you have a more severe meniscus tear such as a bucket handle tear, arthroscopic surgical procedures may be necessary to repair it. The aim of surgery is to preserve as much of your meniscus cartilage as possible.
The procedure itself normally involves stitching the torn cartilage. The success of the surgery depends not only on the severity of your tear but also on your age, and physical condition. The younger and fitter you are, the better the outcome is likely to be.
Following surgery, a rehabilitative exercise program will be outlined for the patient which may include strengthening and balance training. Full cooperation with the rehabilitative technique will be necessary to maximize recovery.
Read more on knee meniscus rehabilitation.
- Andrish JT1. Meniscal Injuries in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis and Management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996 Oct;4(5):231-237.
- Kocher MS, Klingele K, Rassman SO. Meniscal disorders: normal, discoid, and cysts. Orthop Clin North Am 2003;34(3):329–40.