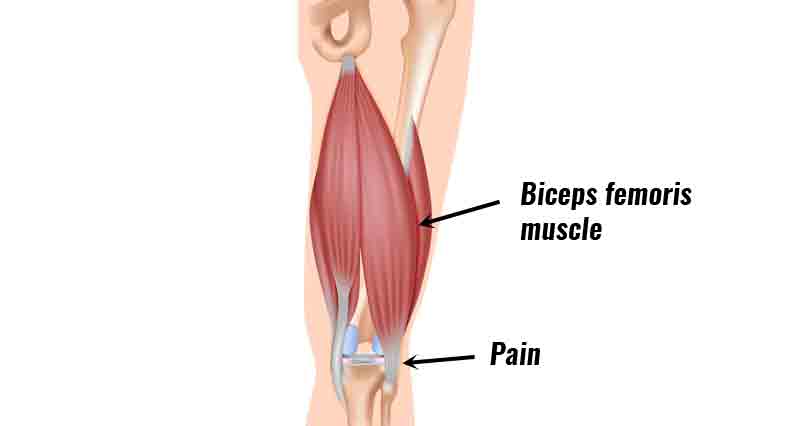
A Baker’s Cyst or Popliteal cyst is a prominent swelling at the back of the knee. It is caused by an underlying injury or condition in the knee joint.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 21st Dec. 2021
Symptoms
A Baker’s cyst is a rounded swelling at the back of the knee. It is often about the size of a golf ball but can vary over time. Symptoms include:
- A sensation of pressure in the back of the joint may radiate into the calf muscle.
- Difficulty bending the knee.
- If you shine a torch through the lump, you should see a red glow around it. This indicates it is filled with fluid.
What is a popliteal cyst?
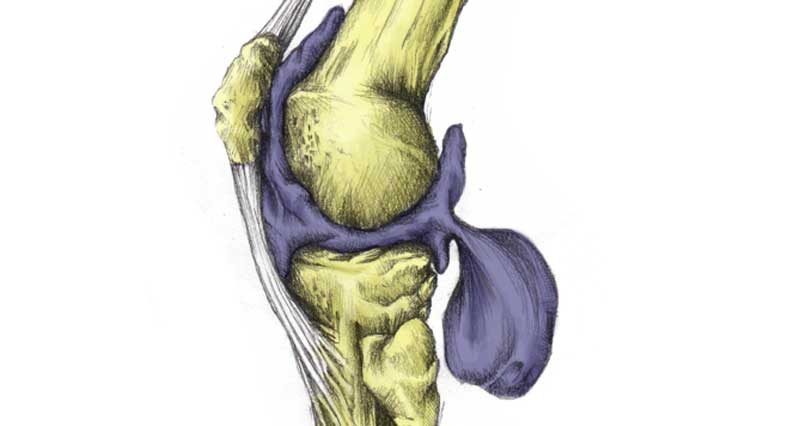
A popliteal or Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that protrudes out the back of the knee.
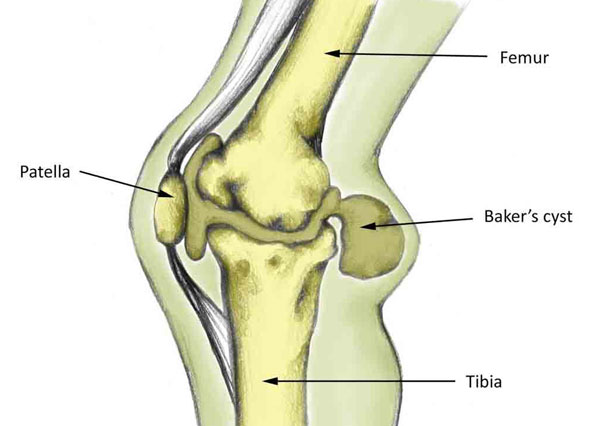
In the hollow at the back of the knee is a bursa (small sack of fluid). The purpose of the bursa is to help lubricate the joint. When the back of the knee joint becomes swollen it causes the bursa to swell as well.
Usually, some underlying disorder of the knee such as a meniscus injury or arthritis causes an increase in synovial fluid. This is the knee’s natural lubricating fluid.
If too much fluid is produced, it spills into the bursa at the back of the knee. As a result, it increases in size, swelling up. Therefore causing a Baker’s cyst.
In younger athletes the cause may be a torn cartilage meniscus may be the underlying cause. In older athletes, arthritis is more likely to be a possible cause.
Treatment for Baker’s Cyst
What can the athlete do?
Rest is important. Avoid any activities which aggravate or make the condition worse.
Change training methods if possible for example substitute swimming, cycling, or cross-trainer machine for running.
It is possible the symptoms may simply disappear by themselves.
In children, the condition may just suddenly clear up however if it doesn’t then surgery is an option. However, there is a 40% chance of the cyst returning.
Try wearing a compression, wrap or knee support to help reduce the swelling.
If symptoms do not clear up on their own then seek professional advice and have a full knee examination to identify the cause of the cyst or swelling.
What can a sports injury specialist or doctor do?
They will examine the knee and diagnose what is causing the swelling in the first place.
For more serious cases a surgeon may operate to correct whatever might be causing the swelling including cartilage meniscus, foreign bodies, or bursa that may need removing.
The patient is likely to be out of action for 8 to 12 weeks following surgery.
Be aware that lumps in the back of the knee are most likely a Popliteal Cyst but might possibly be a tumour or an aneurysm (swelling of an artery). If unsure always seek professional advice.