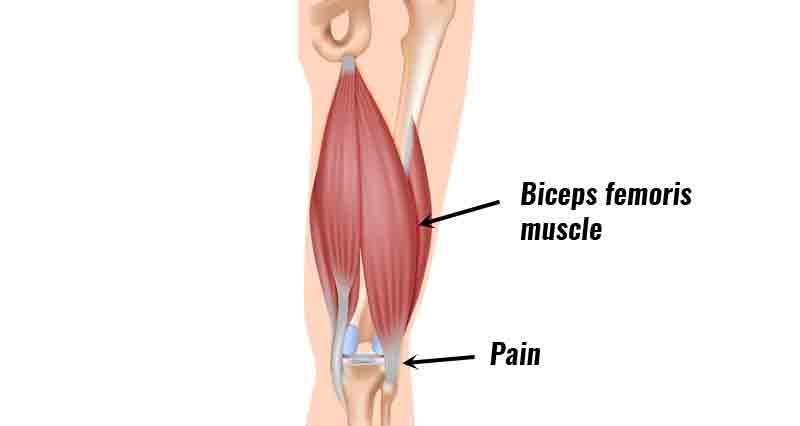
Hamstring tendonitis/tendinopathy is inflammation or degeneration of one of the hamstring tendons at the point where it attaches to the back of the knee. This occurs most commonly in the tendon of the biceps femoris muscle.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 8th Dec. 2021
Symptoms of biceps femoris tendinopathy
- Tenderness and swelling over the outside back of the knee.
- Pain is likely to have come on gradually. You may have had a ‘niggle’, or restriction that you have put up with for some time.
- You may feel stiffness at the back of your knee, which is often worse in the mornings, or after sitting for long periods.
- Often, when your tendon warms up pain eases off, only to return later.
Assessment tests
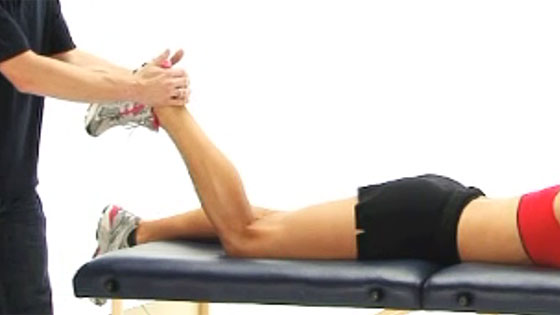
A professional therapist will do a number of assessment tests and take a full case history to understand your injury. In particular, ‘resisted knee flexion’ (trying to bend your knee against resistance) may reproduce symptoms at the back of your knee. You may also show signs of tight hamstring muscles.
Causes & anatomy
Hamstring tendonitis (or tendinopathy) is caused by overuse, or develops from a tear which fails to heal properly.
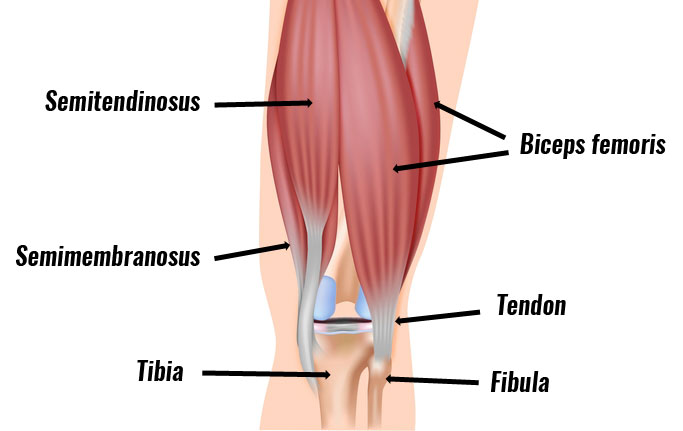
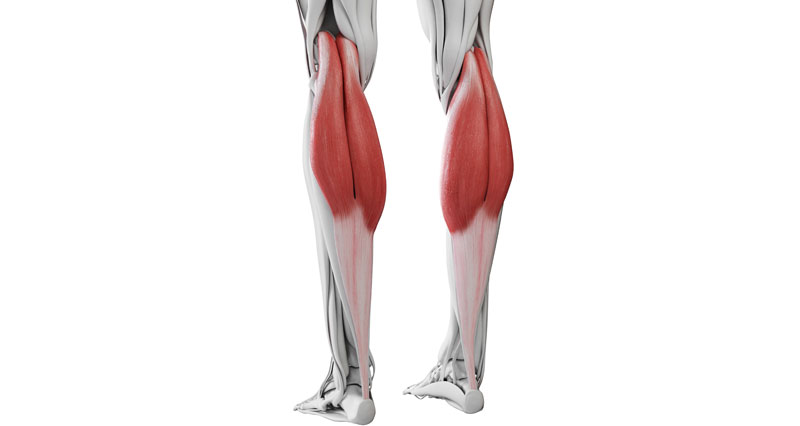
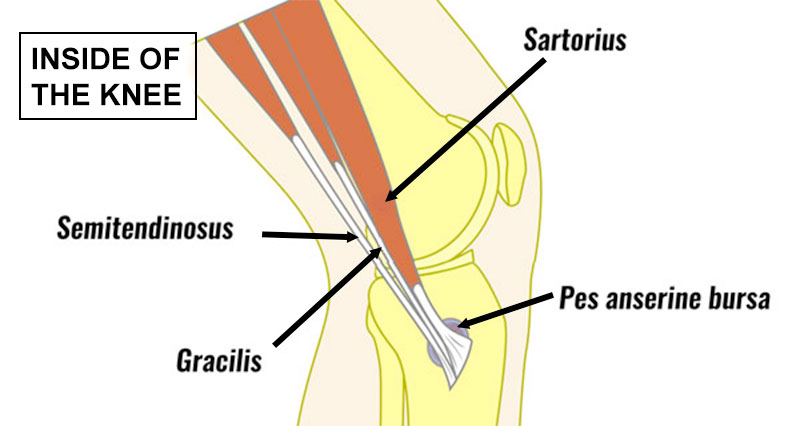
The hamstring muscles
The hamstring muscle group consists of the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus muscles. These muscles strongly bend the knee, and extend the hip backwards.
A great deal of force is put through the hamstring muscles at speed when sprinting and jumping. In particular, at the point just before your foot touches down when sprinting. This is because the muscles work eccentrically (contracting whilst also lengthening) to slow the forward movement of your lower leg.
Mechanism of injury
Inflammation or degeneration of the biceps femoris tendon occurs at the points it inserts into the tibia (shin bone) and fibula. This is a result of overuse, or may also develop after a partial rupture of your tendon which has not healed properly. Most commonly it is the biceps femoris tendon that is involved.
Tendonitis or tendinopathy?
The term tendonitis is most commonly used, however usually this is not strictly accurate. Tendonitis refers to an acute inflammation of the tendon where in actual fact unless the injury is very recent the pain is more likely due to long-term overuse and degeneration of the tendon. A broader and more accurate term for this type of tendon injury is tendinosis or tendinopathy.
Treatment of hamstring tendonitis
Treatment for hamstring tendonitis involves reducing pain and inflammation followed by a gradual rehabilitation program.
Cold therapy
If your injury is recent or acute then rest and apply ice or cold therapy for 10 to 15 minutes every hour for the first 24 to 48 hours.
Medication
Anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen reduces pain, swelling, and inflammation in the early stages. However, this is less appropriate in the later stages of rehabilitation. Check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking medication.
Knee supports
Wear an elastic type of support to help reduce any swelling and support the knee joint.
Later, once the initial acute stage has passed, or if the injury is a long-term chronic condition then applying heat and wearing a heat retainer type knee support is likely to be more beneficial.
Electrotherapy
Applying ultrasound or laser treatment can also help with the inflammation and healing process.
Massage
Cross-friction massage techniques applied to the tendon are sometimes used. Deep tissue massage to the hamstring muscles themselves helps improve the overall muscle condition.
Exercises for hamstring tendonitis
Once pain and swelling have gone, stretching and strengthening exercises can begin to restore the muscle and tendon to full fitness and make it stronger to prevent the injury from recurring.
Gradually increase the load through the tendon so it can cope with the normal demands of sports.
- Eccentric exercises where the muscle contracts as it lengthens are very beneficial in treating tendinopathies.
- Exercises to strengthen the hip muscles, in particular, the large gluteus maximus muscle may also be beneficial.
Preventing hamstring tendonitis injuries
Always ensure you follow a correct warm-up before training or competition. Stretch the hamstring muscles both before and after training. Stretch every day, regardless of whether you are training or not.
Strengthen the muscles to cope with the demands placed on them. In particular eccentric strengthening is important.
Have regular sports massage to keep the muscles and tendons in good condition. Avoid doing too many accelerating/decelerating runs or hill work.
Similar/related injuries:
- Biceps femoris tendon avulsion is where the tendon pulls a small piece of bone away with it.
- A hamstring strain is a tear to any of the hamstring muscles.