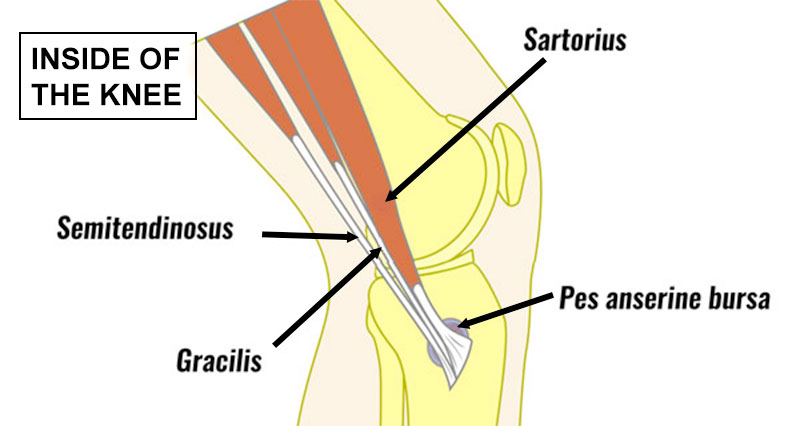
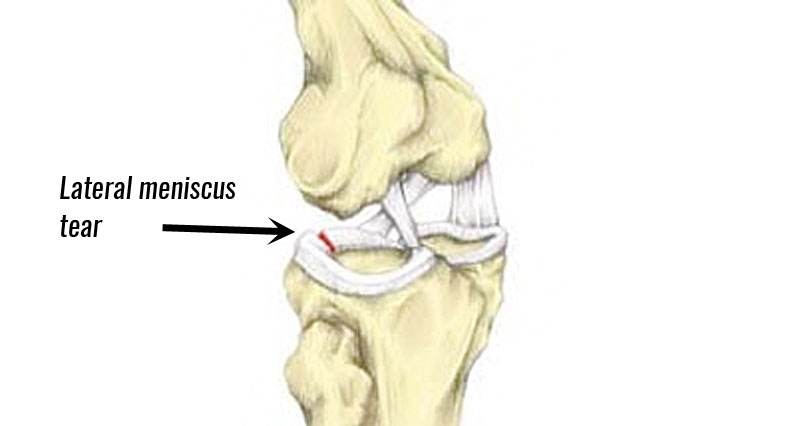
Coronary ligament sprain has similar symptoms to a cartilage meniscus injury. It often occurs at the same time as lateral knee ligament injuries.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 31st Dec. 2021
What is a Coronary ligament injury?
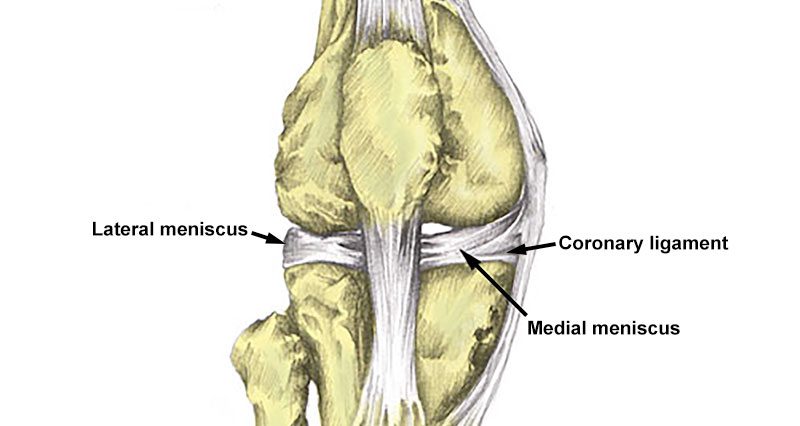
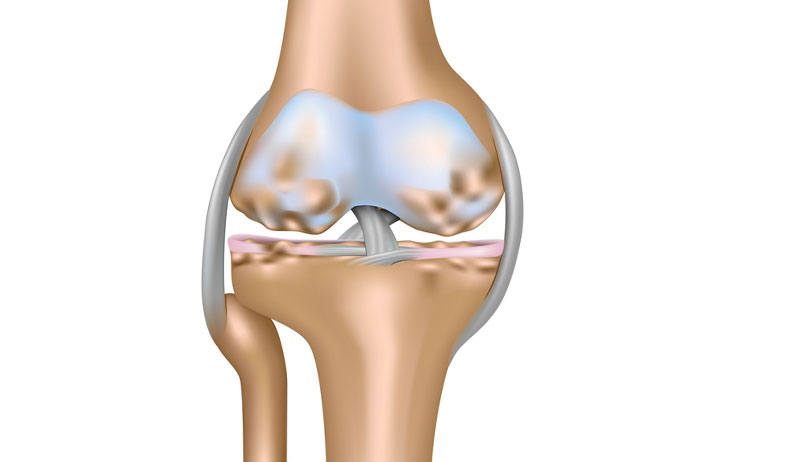
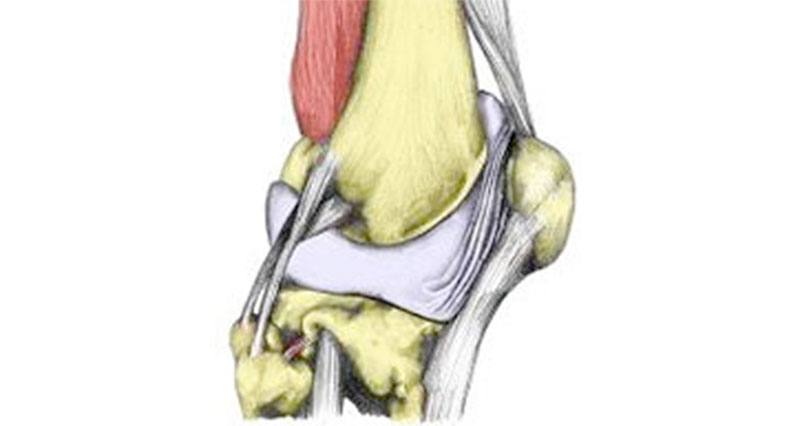
There are two coronary ligaments in the knee. Sometimes called the meniscotibial ligaments they form part of the fibrous joint capsule which surrounds the joint.
They are located on the medial (inside) and lateral (outside) of the joint and attach to both the edge of the cartilage meniscus and the tibia. Their purpose is to fix the cartilage meniscus to the bone and limit knee rotation.
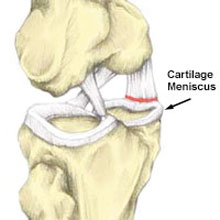
Coronary ligament injuries are usually acute, sudden-onset injuries that occur when twisting the knee. For example, suddenly changing direction with your foot firmly planted on the floor.
They can however also occur as a result of overuse or repetitive strain, especially in sports that involve twisting at the knee, such as soccer, martial arts, and dancing. They frequently occur in association with other knee joint injuries, in particular:
Symptoms of a coronary ligament sprain
A coronary ligament sprain has very similar symptoms to that of a torn meniscus. It is often difficult to differentiate between the two. Symptoms include:
- Sharp pain on twisting movements with tenderness along the joint line of the knee.
- Little or no local swelling along the joint line. No joint swelling.
- Painful or tenderness pressing in along the joint line.
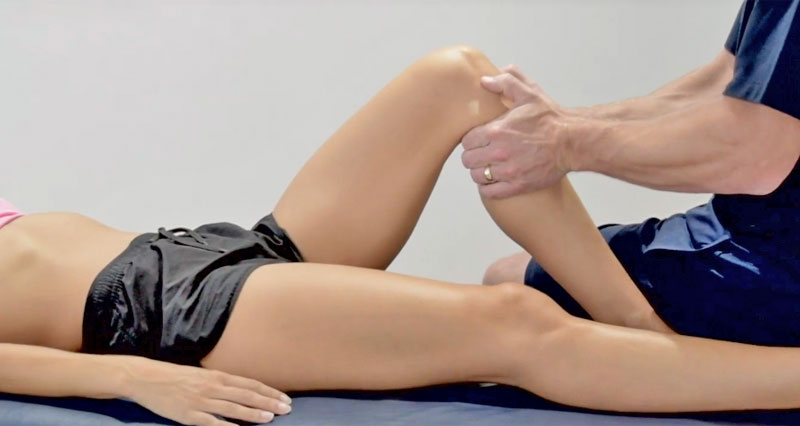
- McMurray’s test may give a positive result.
- The end-of-the-range motion may be uncomfortable.
Imaging
An MRI scan may help diagnose a Coronary ligament sprain. However, not always. Therefore, if it is not obvious then you may need arthroscopic surgery to investigate whether you have a ligament sprain or a meniscus injury.
McMurray’s test
Coronary ligament sprain treatment
Treatment varies depending on how bad your injury is and which other structures in the knee joint are injured.
Rest
Rest from aggravating activities. Complete rest may not be necessary depending on how bad the injury is but avoiding any activities that trigger pain is important.
In many cases, this may just mean modifying training to avoid any sideways or lateral movements, twisting, and turning. A straight-line running may be possible but switch to cycling or running in a swimming pool until pain-free if necessary.
Cold therapy
Apply cold therapy to ease pain, inflammation, bleeding, and swelling if there is any.
Knee supports
Wear a hinged or stabilized knee support. These have extra supports at the side to restrict lateral (sideways) movement.
Medication
Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication, for instance, ibuprofen.
Exercises
When pain allows, begin a full rehabilitation program. This should include mobility, activation, strengthening, movement control, and functional exercises.
Read more about knee rehabilitation exercises for medial meniscus injuries.