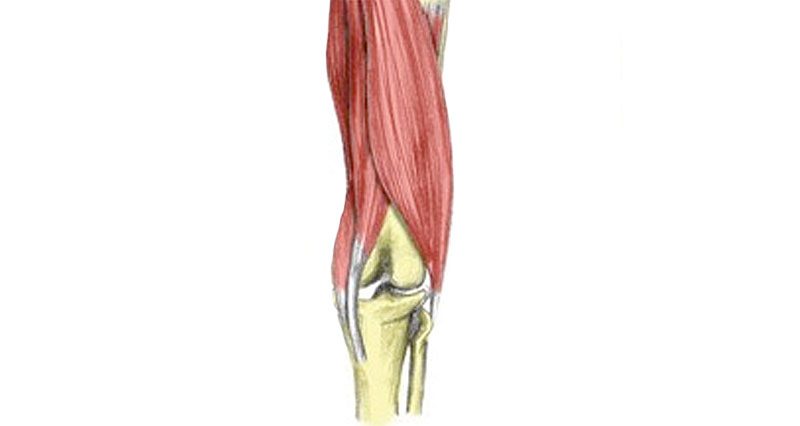
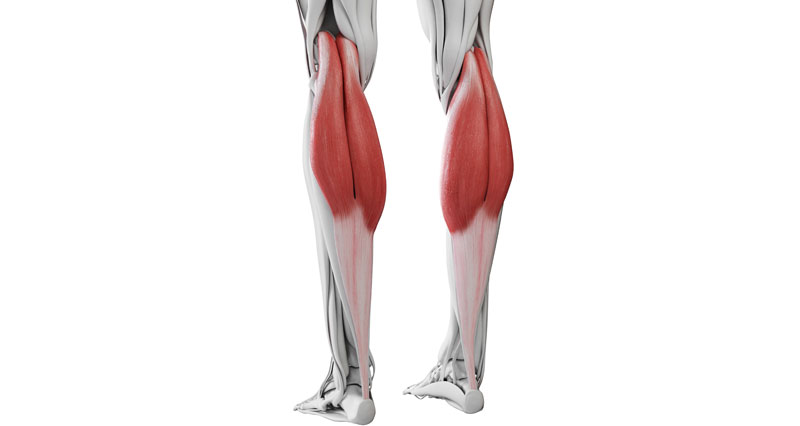
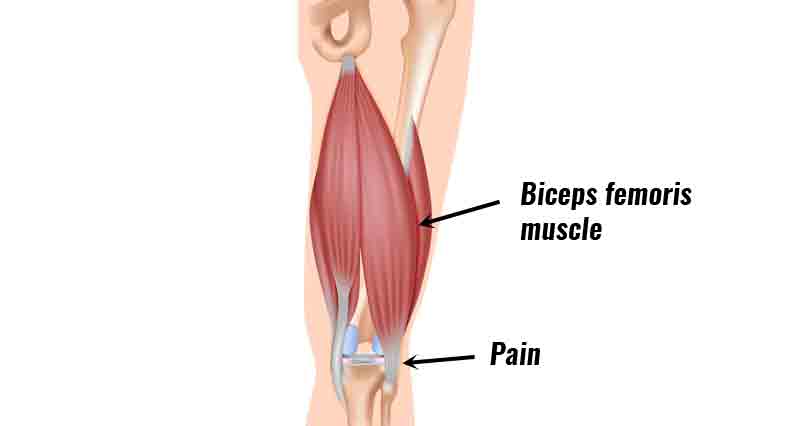
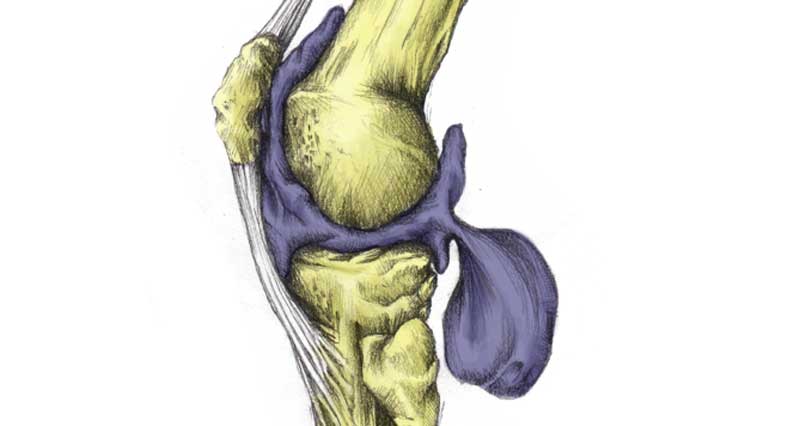
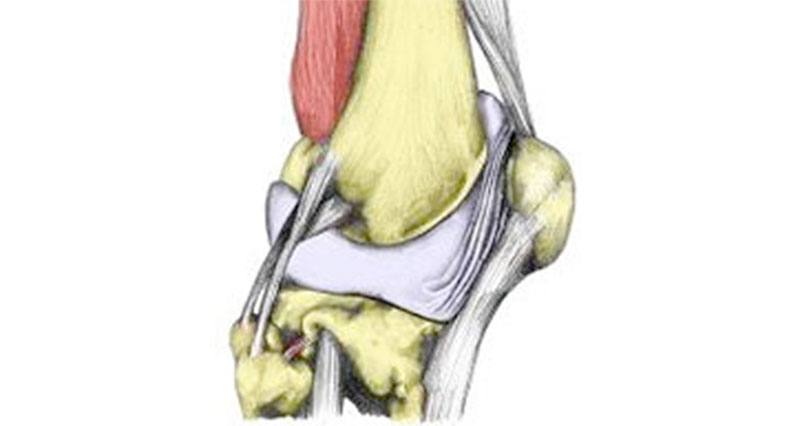
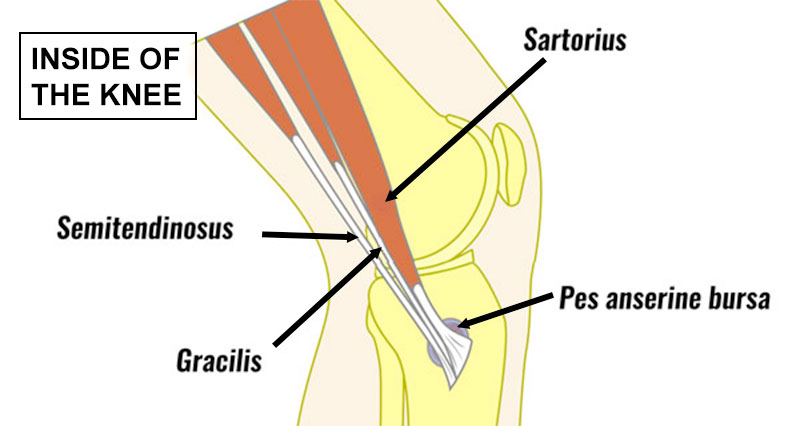
A hamstring tendon strain is a tear or rupture of a hamstring tendon at the back of the knee. The most common is a Biceps femoris tendon strain. A hamstring avulsion strain occurs if the tendon pulls a small fragment of bone with it.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 31st Dec. 2021
Symptoms of hamstring tendon strain
Symptoms include:
- Sudden sharp pain in the back of the knee.
- There may be swelling, tenderness and heat at the back of the knee.
- You may feel pain flexing (bending) your knee against resistance.
- Local swelling at the point of injury.
- Significant loss in hamstring muscle strength.
An avulsion strain (or fracture) has similar symptoms consisting of a sudden sharp pain at the back of the knee. This is particularly painful so continuing to play on is not usually an option.
With an avulsion strain, it may even be possible to feel the bone fragment through the skin.
Imaging
If you suspect an avulsion injury then seek professional medical advice immediately. An X-ray confirms the diagnosis.
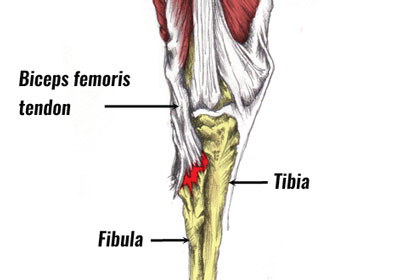
Hamstring tendon strain causes & anatomy
The hamstring muscles consist of three muscles called the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. Their function is knee flexion (bending the knee) and hip flexion (moving the thigh backwards). The muscles insert at the back of the knee via tendons that join muscle to bone.
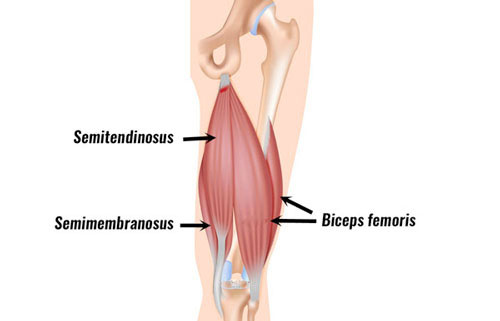
It is possible to tear the tendons during explosive movements or kicking. In particular, the biceps femoris tendon or the semitendinosus tendon. A great deal of force passes through the hamstring muscles when sprinting. This is because they work hard to slow down the lower leg as it comes through and strikes the ground.
Buy Knee Braces
Previous hamstring tendinopathy which has failed to heal properly could be a weak point. As a result, making you more susceptible to injury.
Treatment of hamstring tendon strains
What can the athlete do?
Apply cold therapy or PRICE principles (protection, rest, ice, compression, elevation) as soon as possible. Ice is applied for 10 minutes every hour during the acute stage.
This is usually 24 to 48 hours depending on how bad the injury is. Do not apply ice or a gel ice pack directly to the skin but wrap in a wet tea towel. Even better is to use a commercially available cold therapy and a compression wrap.
Seek professional advice if you suspect an avulsion strain or a complete rupture of the tendon.
If the injury is to the semitendinosus muscle on the inside back of the knee then it is likely this will be treated conservatively, meaning without surgery. However, in more severe cases a torn biceps femoris tendon may require an operation to fix it.
After the first 2 or 3 days when the tendon has started to calm down, alternate hot and cold. Commercially available gel packs are ideal for this purpose as they can be warmed in hot water carefully in the microwave, or frozen.

Buy Knee Braces
Wear knee support to support to protect the tendon and retain the body’s heat which will aid the healing process. When returning to running a heat retainer or support can be worn. Tendons work better when they are warm but as a precaution applying ice after a training session can help reduce any inflammation.
What can a sports injury specialist or doctor do?
A doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen to help with the pain and inflammation in the early stages. Do not take Ibuprofen if you have asthma or other contraindications, always check with a medical professional first. Anti-inflammatory medication may not be as effective in the later stages and may even restrict healing.
For very severe tendon strains and complete ruptures, the knee may be immobilized in a plaster cast or a surgeon may operate to repair the damaged tendon.
Sports massage may be beneficial in remodelling the scar tissue and improving the condition of the hamstring muscles themselves. Cross-friction massage is applied by rubbing transversely across the tendon.
A full rehabilitation program consisting of stretching, and strengthening exercises should be done to restore the athlete to full fitness.
Exercises
In the case of mild tendon injuries, stretching and strengthening exercises for the hamstring muscles can begin when pain allows. But beginning exercises too soon, or if an avulsion fracture is present could make the injury worse. Stretching, strengthening, and finally functional or sports-specific exercises all play a part in the rehabilitation of hamstring tendon strains.
See hamstring strain rehabilitation exercises for more detailed information.