Osteoarthritis, is wear and tear, in the knee joint. It is a common cause of gradual onset knee pain and joint stiffness. In particular, it affects people over 50 years of age, especially women.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 31st Dec. 2021
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis in the knee
Symptoms include:
- Deep aching pain in the inner knee.
- Pain is often worse after exercise.
- Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning, however, often reduces with movement.
- Swelling.
- Sometimes a clicking or cracking noise when you bend your knee.
Diagnosis
To diagnose osteoarthritis the clinician might assess the nature and severity of pain. They will measure the amount of movement in the joint and take an X-ray of the knee.
Narrowing the joint space is a good indicator of osteoarthritis. Bony spurs can also be seen on an X-ray.
In certain cases, a blood sample may be necessary to rule out the presence of other types of arthritis.
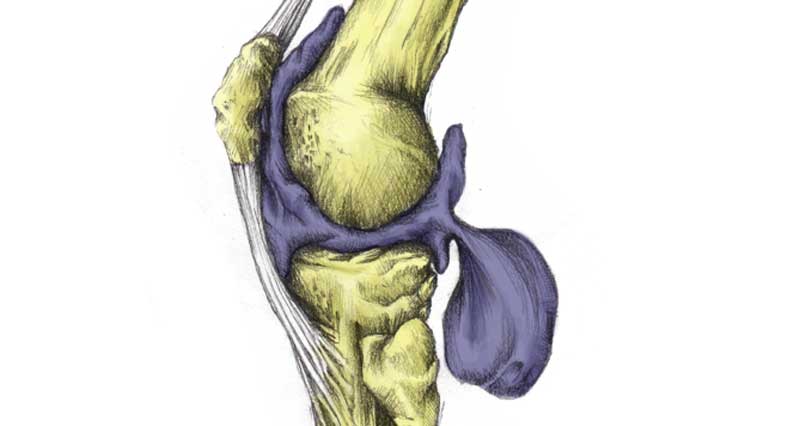
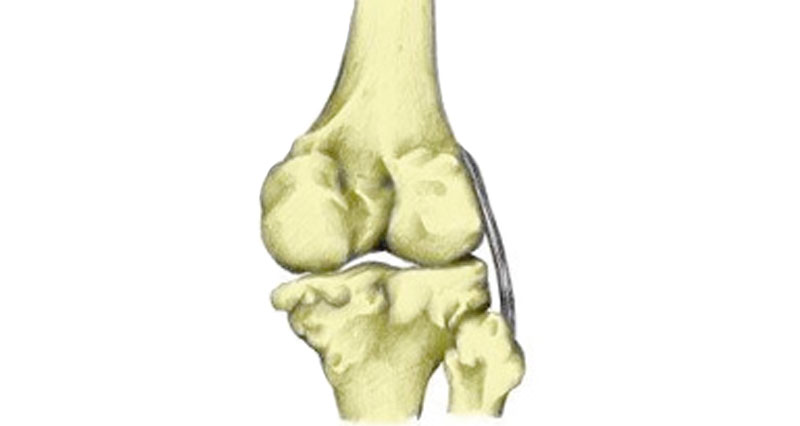
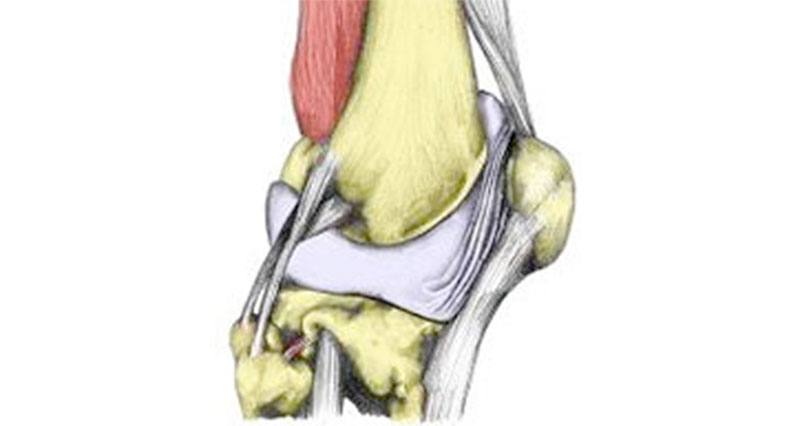
Anatomy
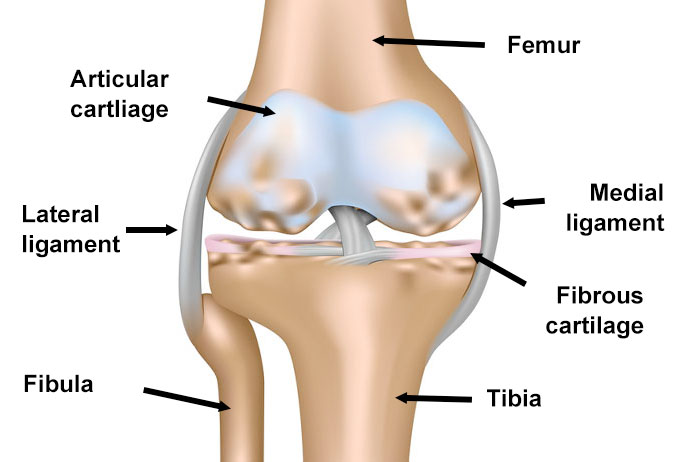
Articular cartilage is a smooth, hard, fibrous tissue that covers the ends of bones. Also known as hyaline cartilage its function is to protect the ends of the bones and lubricate the joint movement.
In the knee, there are two semi-circular discs of fibrous cartilage called menisci. They provide support and cushioning for the knee.
The synovial membrane surrounds the joint and produces a lubricating fluid called synovial fluid.
What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis (also called degenerative joint disease) is wear and tear of the joint. More specifically, of the articular cartilage. As the disease progresses, the cartilage itself becomes thinner and in some cases may wear away altogether. As a result, the bone itself starts to wear.
In addition, the bones themselves become thicker and may form bony “spurs”. The synovial membrane also becomes inflamed.
All of these factors cause pain and impaired movement in the joint. Osteoarthritis can form in any joint but is more common in weight-bearing joints such as the knee and hip.
Who is most at risk?
Osteoarthritis of the knee is common in people over 50 years of age, in particular in women. It can affect either one knee (unilateral) or both knees (bilateral).
Osteoarthritis occurs in the inside of the knee (medial) or the outside (lateral) aspect of the knee. However, it occurs more commonly on the inner (medial) aspect of the knee.
Knee osteoarthritis is common in individuals who play intense physical sports, such as football. The previous injury to the knee is a strong indicator of the development of osteoarthritis in the future. Symptoms develop slowly over a number of years.
Causes
Causes of osteoarthritis include a history of acute injury to the medial knee. For example, meniscal or ligament trauma, and prolonged and excessive use of the knee joint.
Previous fractures at the site of the knee joint, obesity, and genetic factors can all play a role in the development of osteoarthritis.
Treatment of arthritis in the Knee
As yet there is no cure for arthritis. However, a number of treatments may slow the progression of the disease.
Buy Knee Braces
Knee braces
Simple compression knee supports for arthritis are great for providing support and relieving pain. However, specialist knee supports or braces known as valgus unloader braces work by reducing the load on the inside of the knee.
Medication
NSAIDs- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs such as ibuprofen can provide some temporary pain relief.
Hot & cold therapy
Hot and cold treatments applied to the knee can help with relief from pain and inflammation after exercise.
Weight loss
If you are overweight, then losing weight helps slow the progression of Osteoarthritis.
Exercise
Exercise programs help to maintain healthy cartilage and range of motion of the joint. In addition, keeping muscles and tendons conditioned and strong helps joint stability. If weight-bearing exercising is difficult, cycling or hydrotherapy may be useful to reduce the stress on the joints.
Joint lubrication
A viscosupplement is administered as an injection by a clinician. This substance a gel-like fluid called hyaluronic acid helps to lubricate the knee joint and can decrease the amount of inflammation.
Surgery
Extreme cases may benefit from knee replacement surgery. Both half and total knee replacements are available.