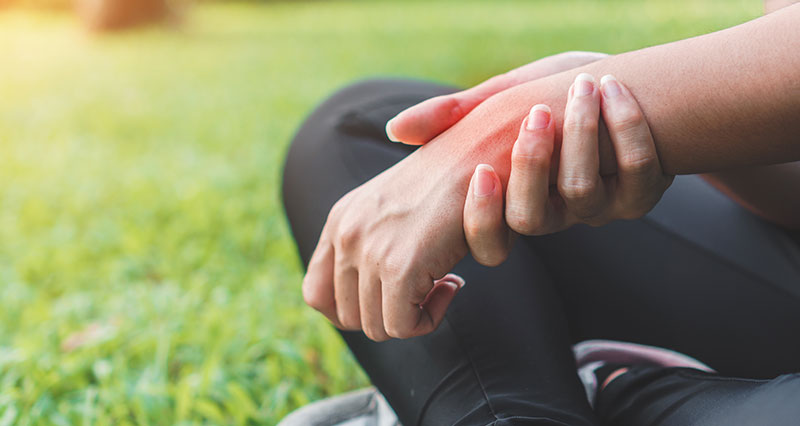
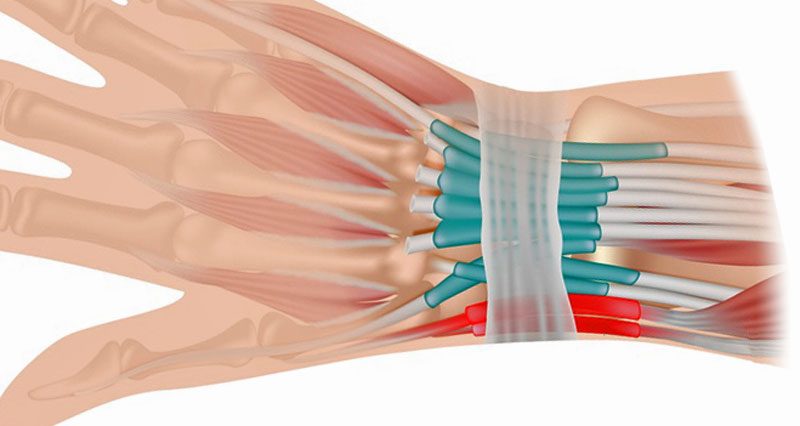
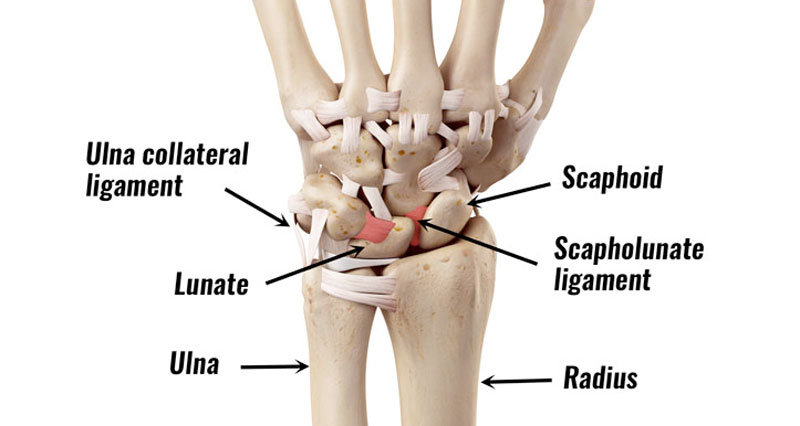
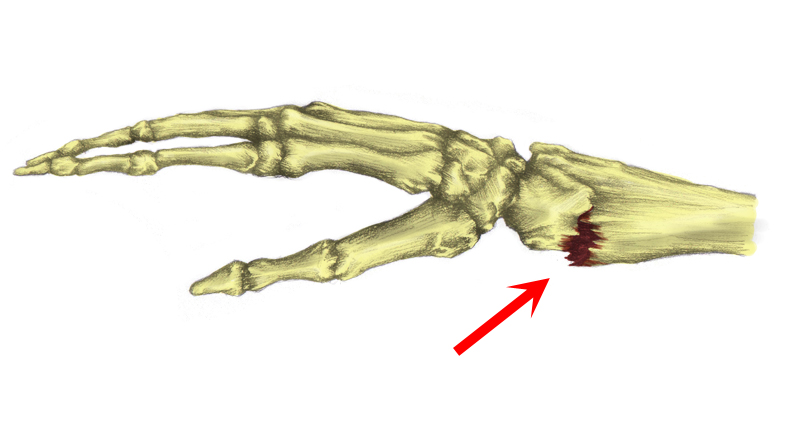
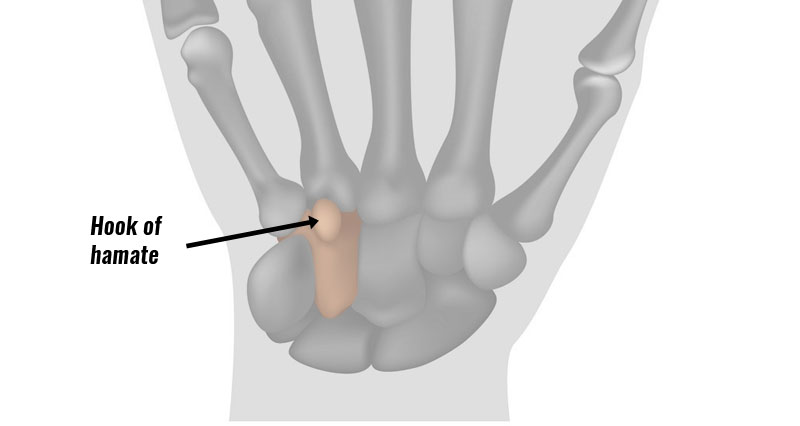
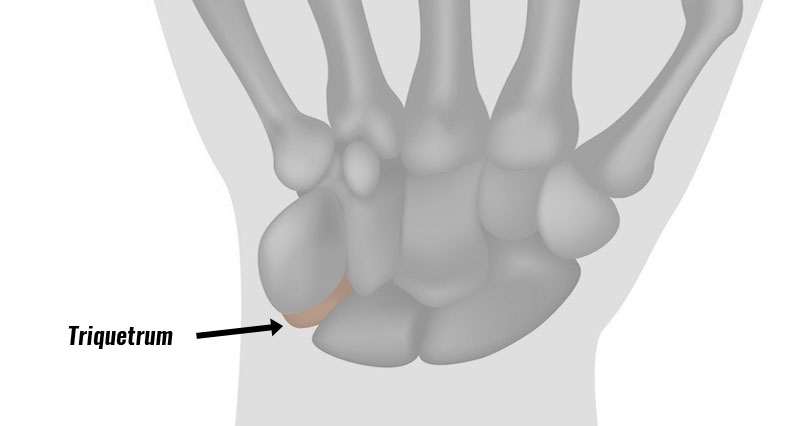
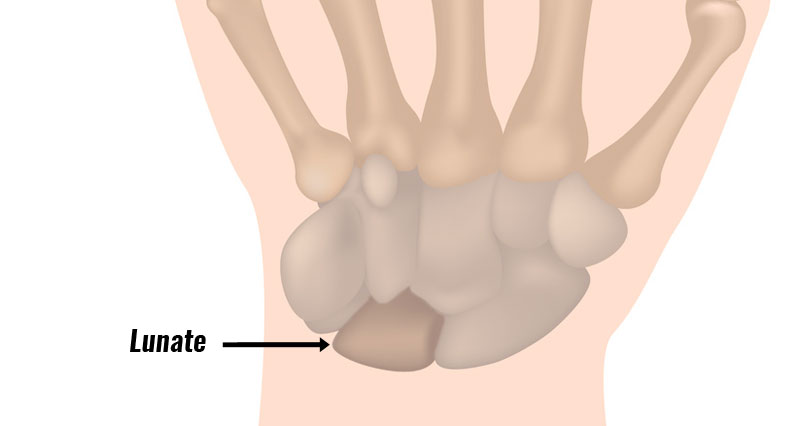
Wrist tendonitis is inflammation of tendons in the wrist. It is an overuse injury resulting in gradual onset pain and stiffness. In most cases it is more likely to be degeneration or wear and tear of the tendons. Therefore, tendinopathy is probably a more accurate term.
Wrist tendonitis symptoms
- Symptoms of wrist tendonitis include pain in the wrist, along with stiffness in the mornings.
- The wrist will be tender when pressing in over the injured tendon.
- Swelling may be visible over the painful tendon.
- A creaking sensation in the tendon called crepitus may be felt when moving the wrist, particularly if it is an old injury.
Causes of wrist tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis is an overuse condition that occurs due to repetitive strain or friction of the tendon. In particular, when a tendon rubs over a bony prominence friction causes inflammation.
This is different from a wrist sprain, which is an injury to a ligament that connects bone to bone, whereas tendons connect bone to muscle.
This injury is commonly called tendonitis. However, often this is often technically incorrect. The term tendinopathy is more appropriate and describes a degeneration of the tendon rather than an inflammation. Investigations and biopsies have often found no inflammatory cells present. Wrist tendonitis symptoms and treatment are usually the same, whether the injury is inflammation or degeneration.
Activities which require repetitive wrist movements are most likely to contribute to the development of wrist tendonitis which is a form of repetitive strain injury. Examples include sports such as badminton and jobs such as working a production line. Tendon injuries to the wrist can also occur suddenly (acute wrist injuries) through an impact or fall which also causes injury to ligaments and other tissue.
Treatment
Rest from aggravating activities. Continuing to use the wrist when it is painful will prevent healing and could make the injury worse. If you fail to treat your injury properly in the early stages, it may become chronic. As a result, it is much more difficult to treat.
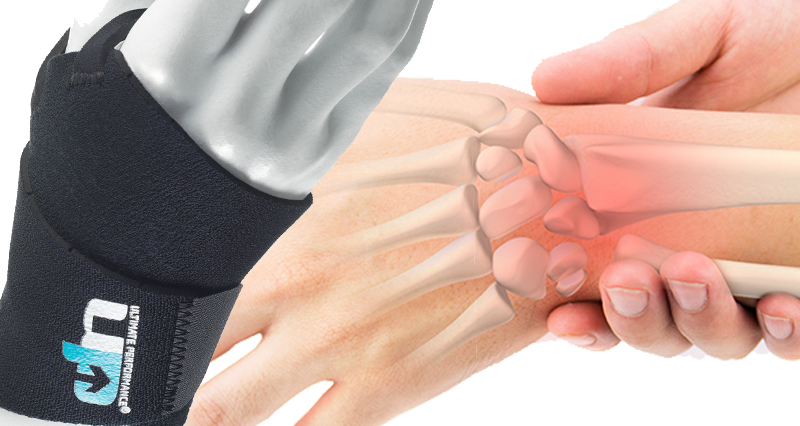
Wearing a wrist splint or support may help with resting, particularly if you need to use your hands. By immobilizing the wrist the tendons have to work a lot less and have a chance of healing.
Apply cold therapy to ease pain and swelling, particularly in the early days or when wrist tendonitis is very painful. Later if the injury is chronic then heat may be more beneficial.
Your doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen. Do not take ibuprofen if you have asthma. Always check with a doctor before taking medication.
If this fails a corticosteroid injection may be given although probably not more than once. Injecting tendons in the hand and wrist can weaken them long-term.
If this is also unsuccessful, wrist surgery may be needed. The aim of surgery is to release the tendon from its sheath and to remove, and adhesions from the tendon, allowing it to move more freely, thus reducing friction and degeneration.