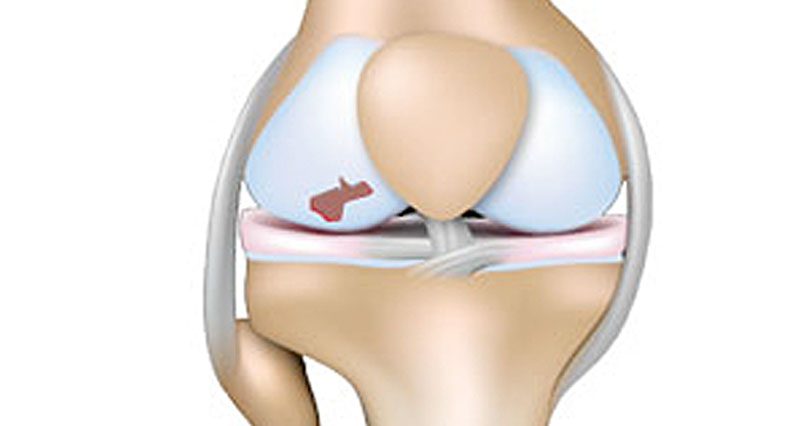
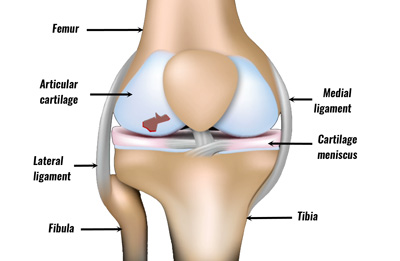
Articular cartilage injury is damage to the tough, thin cartilage that lines the ends of bones. It is often caused by a collision or trauma to the knee or in conjunction with other knee joint injuries.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 2nd Jan 2022
Symptoms of articular cartilage injury
Symptoms consist of:
- Recurrent pain and swelling in the knee joint.
- Locking of the knee due to loose bodies floating within the joint.
- The patient may also experience audible clunks and clicking noises when moving the knee.
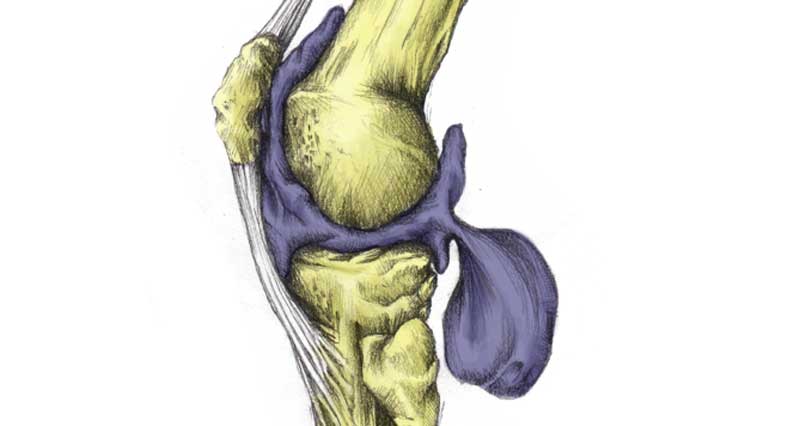
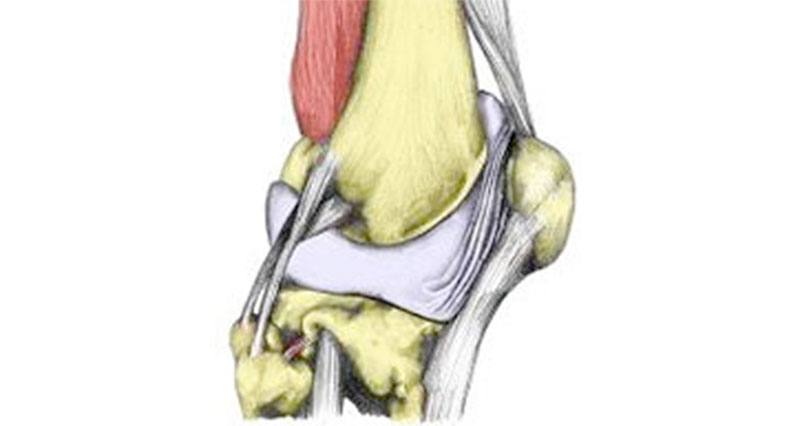
Articular cartilage injury explained
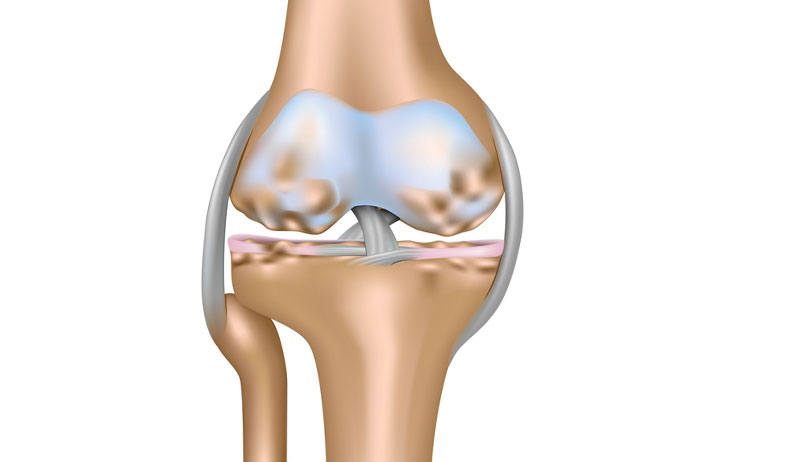
Articular cartilage or hyaline cartilage is a very smooth, hard material that lines the ends of bones. Its purpose is to protect the ends of the bone and allow smooth movement between the surfaces of bones. In addition, articular cartilage is extravascular.
In other words, it has no direct blood supply. Therefore, once injured it is extremely slow to heal.
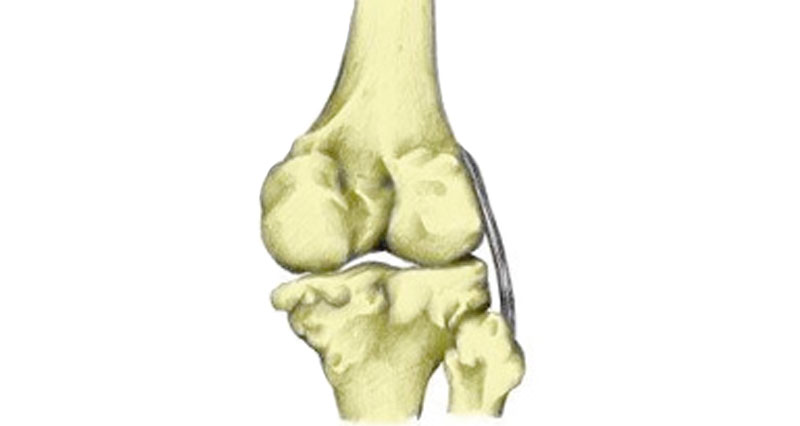
Damage can occur to the articular cartilage on its own, or in conjunction with other knee injuries. For example, Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries from twisting. This is due to the fact that one of the ACLs functions is to prevent rotation of the knee. When twisting, the surfaces of the femur and tibia become damaged.
Impact or trauma to the knee also results in injuries such as PCL tears as well as cartilage meniscus injury and patellar dislocations. All of which are associated with an articular cartilage injury.
Articular cartilage injury leads to inflammation and pain in the knee joint. Long term this accelerates the onset of Osteoarthritis.
In more severe cases damage to the articular cartilage also leads to fractures in the bone lying immediately below it (called subchondral bone). As a result, an osteochondral Fracture or osteochondritis dissecans. This is especially common in adolescents where the bone fragment becomes dislodged.
Treatment of articular cartilage injuries
Apply RICE or rest, ice, compression, and elevation to help minimize swelling. Cold therapy or ice can be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every hour in the acute stage which is usually the first 24 to 48 hours. After that reduce the frequency as the swelling goes down. A specialist cold therapy knee wrap is ideal for applying both cold therapy and compression to the knee together.
A doctor may prescribe NSAIDs, e.g. Ibuprofen, to address pain and swelling. A sports injury professional can correctly diagnose the injury and extent of the damage which may require an X-ray or arthroscopy. Arthroscopy is an operation where they look inside the joint to determine the extent of the injury.
If the injury is not severe then conservative management may involve rest for a number of weeks followed by gentle exercise rehabilitation. In more serious incidences, in particular, those having sustained a fracture or osteochondritis dissecans surgery may be necessary to fixate the detached fragment.
Another surgery involves attempts to stimulate the recovery of the articular cartilage itself such as recruitment of marrow stem cells into the affected area by piercing the subchondral bone.