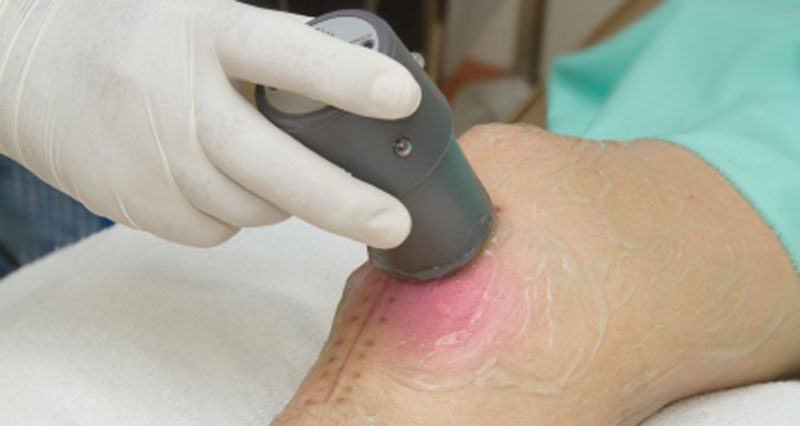
Electrotherapy is the use of electricity as a form of treatment for soft tissue injuries. Interferential, Laser, Magnetic field, Ultrasound, Shortwave and Shockwave therapy are common methods in sports injury treatment.
Interferential
A form of electrotherapy, Interferential uses two alternating medium frequency currents. The two currents form an area of wave interference where they cross. This results in a modulated frequency equal to the difference in frequency of the two waves.
It stimulates the muscle in a similar way to a normal muscle contraction. It helps to reduce pain in the same way as TENS, using the pain-gate theory. it also affects circulation. At low frequencies of 0-10 Hz muscle stimulation occurs which helps remove any build-up of swelling. At higher frequencies, of 90-100 Hz, vasodilation occurs and increases the blood flow to the area to help heal.
What is Interferential be used for?
Interferential therapy treats a large range of musculoskeletal injuries, especially where swelling and muscle spasms are present. interferential stimulation can effectively treat joint pain. Specific injuries include back pain, frozen shoulder, patellofemoral knee pain, meniscus injuries, sacroiliac joint pain….the list goes on!
What are the Contraindications?
Do not use Interferential in the following situations:
- When there are sensory disturbances
- Local infection
- Malignant tumors
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Circulatory conditions
- Over or near a pacemaker
- Pregnancy
Laser Therapy
Laser stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers produce pure light by a series of reactions.
What is Laser Therapy?
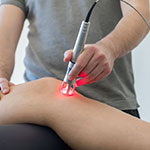
We use low to mid powered lasers in therapy. They produce up to 50 mW of power and therefore, produce little or no heat. This is why they are called cold lasers.
There are two types of laser in the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries:
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) which is not visible.
- Helium-Neon (HeNe) which has a lower wavelength and is visible.
The settings and dose used, depends on the depth of the injury, amount of fatty tissue overlying the injured structure, and the age of the client. Laser appears to be of most benefit in tendinopathy-type injuries.
What is Laser be used for?
Laser therapy treats of all kinds of musculoskeletal injuries to help reduce pain, muscle spasms, and inflammation and encourage cell reproduction. Research has however shown that Laser may not be as effective as other forms of electrotherapy.
What are the Contraindications?
Laser should not be used in the following situations:
- Pregnancy
- Malignant tumours
- Treating infants
- Patients receiving photosensitive medication
Magnetic Field Therapy
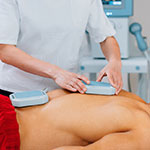
This type of electrotherapy treatment is used regularly in people with chronic pain conditions. Treatment can either be pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) or static magnetic fields (SMF).
What is Magnetic Field Therapy?
PEMF uses an alternating current through a coil applicator, whereas SMF uses simple, static magnets. The most common example is magnetic bracelets and other jewellery which can be purchased from high street pharmacies. Both forms of magnetic field therapy have the effect of decreasing swelling and inflammation.
Practitioners of magnetic field therapy believe that to maintain health and healing, the body’s electromagnetic field must be in balance and the use of magnetic field therapy helps to restore this balance.
What is Field Therapy be used for?
Magnetic field therapy is shown to be successful in producing analgesia (pain relief) in a number of different conditions including lower back pain and osteoarthritis. However, most studies demonstrating a positive effect on pain are of poor quality and so there is no solid evidence promoting the use of magnetic fields in treating injuries or chronic pain.
What are the Contraindications?
You should not use should magnetic field therapy in the following situations:
- Pregnancy
- Tuberculosis
- People with pacemakers
Short Wave Diathermy

Pulsed short wave diathermy is a form of electrotherapy, similar to Ultrasound. It uses electromagnetic energy to heat the underlying tissues. High frequency, short wave, alternating electrical currents pass into the muscles, tendons, ligaments, etc.
As the current alternates between positive and negative, this causes structures within the muscle to rotate in reaction. This friction from repeated movement causes an increase in temperature.
This works in a similar way to ultrasound, however, diathermy can be used to heat a larger area and also heats the deep muscles more effectively. On the downside, diathermy units are expensive and can only be used by one person at a time.
What can Short Wave Diathermy be used for?
- Muscle strains.
- Ligament sprains.
- Tendinopathies (e.g. Achilles)
- Back or joint pain.
What are the Contraindications?
Short Wave Diathermy should not be used in the following circumstances:
- Over metal implants such as pins and plates.
- On the chest of patients with pacemakers.
- Over the abdomen or back of a pregnant woman.
- When infection is present.
- Over open wounds.
- Over cancerous tissue.
TENS

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a method of providing pain relief. As the name suggests, it involves the application of electrical current to the affected area. This is achieved via a number of electrodes that can be fixed on the skin.
TENS relieves pain mainly by stimulating the pain gate mechanism. Electrical signals from the machine block the body’s natural pain signals.
Read more on Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation.
Ultrasound Therapy
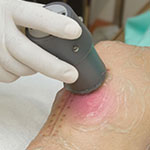
Ultrasound has been used as an electrotherapy treatment modality by therapists over the last 50 years. It transmits high-frequency sound waves into tissues. It has a number of benefits and effects including heat and micro-massage effects.
However, the effectiveness of therapeutic ultrasound is controversial. To date, there is still very little evidence to explain how ultrasound causes a therapeutic effect in injured tissue. Nevertheless, practitioners worldwide continue to use this treatment modality relying on personal experience rather than scientific evidence.
Read more on Ultrasound therapy.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
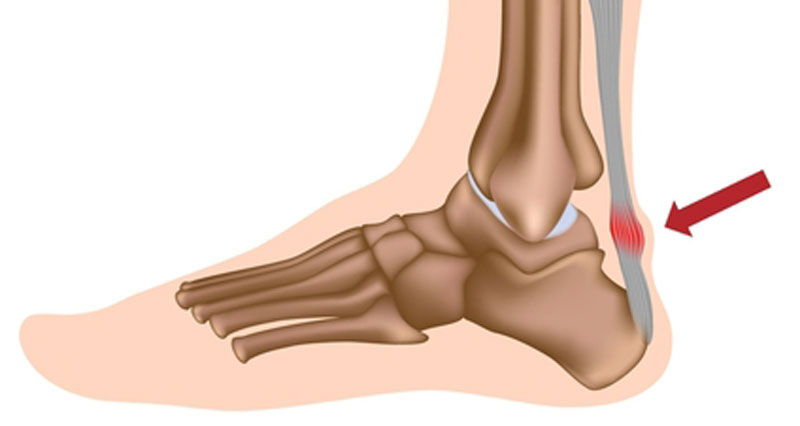
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy is a form of Electrotherapy which has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of tendon injuries such as Achilles Tendinopathy and Tennis Elbow, as well as Plantar Fasciitis.
What is Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT)?
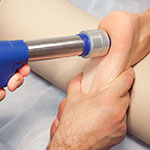
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy is a method of therapeutic treatment for soft tissue injuries. It works by passing shock waves (short but intense energy waves) which travel faster than the speed of sound, into the tissues. Breaking down kidney stones is the original use for shockwave therapy. However, patients receiving this treatment also noticed a decrease in pain from other soft tissue injuries. As a result, the technology has been adapted to be suitable for use specifically in these areas.
What Injuries is it used for?
ESWT is most effective in treating conditions where major tendons connect to bones:
ESWT also encourages bone healing and so can be used for stress fractures.
When should it NOT be used?
In some cases, shock wave therapy is not suitable. Here are the most common examples:
- Application over open growth plates (where there may still be growth)
- Over metal pins or plates etc
- Malignant tumours
- Pregnancy
- Nerve and circulation disorders
- Infections.
How does ESWT Work?
Whilst the exact process is still up for debate, it is thought that ESWT works by causing microtrauma to the tissues which creates neovascularisation – an increase in new blood vessels. These bring an increase in blood flow to the area and therefore aid tissue healing. Beneficial effects may also be down to the stimulation of an acute inflammatory response in a chronic injury. This can effectively re-stimulate the healing process.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy can be either High-level or Low-level energy.
High-Level ESWT
- Applied in a single dose.
- Energy levels above 0.6 mJ/m.
- Can be painful.
- Used in conjunction with local aneasthetic.
Low-Level ESWT
- Requires multiple treatments.
- Energy levels below 0.08 mJ/m.
- Less painful – may be uncomfortable.
- A local anesthetic is not normally used.
Exogen – Ultrasound Bone Healing System
Exogen is a bone healing system that is used in treating fractures, especially those which are not healing naturally. It uses ultrasound waves to stimulate bone healing.
How Does Exogen Work?
Exogen uses a low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) signal to stimulate the natural bone healing process. It is a portable device with a small transducer that you place on the skin over the broken bone. Ultrasound waves pass through the overlying soft tissues to penetrate the bone.
Exogen is simple to use and has a short treatment time of 20 minutes a day. It can be used with casts and is effective even where metal fixations are present
It can be used on recent fractures to accelerate the healing time, as well as on non-union fractures (where the bone is not healing).
Facts and Figures
- Accelerates the healing of broken bones by 38% 1,2
- High heal rate for non-union fractures (no sign of healing observed) – 86%3
- 10 percent of fractures (c. 85,000 fractures per annum) are estimated to be classed as delayed or non-union where slow or no signs of normal healing are observed4
Indications and Contraindications
The Exogen bone healing system is used for:
- Treatment of delayed union and non-unions
- Accelerating the time to heal of fresh fractures
- Treatment of stress fractures
- Accelerating repair following osteotomy
- Accelerating repair in distraction osteogenesis procedures
- Treatment of joint fusion
- Accelerating repair in bone transport
There are currently no known contraindications (when the system cannot be used). Although safety and effectiveness have not been established for children, pregnant women, or patients with pacemakers, fractures from bone cancer, poor circulation, or blood clotting disorders.
Reference Articles
1. Heckman JD, Ryaby JP, McCabe J, Frey JJ, Kilcoyne RF. Acceleration of tibial fracture-healing by non-invasive, low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994;76:2634.
2. Kristiansen TK, Ryaby JP, McCabe J, Frey JJ, Roe LA. Accelerated healing of distal radial fractures with the use of specific, low-intensity ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997;79:96173.
3. Nolte PA, van der Krans A, Patka P, Janssen JMC, Ryaby JP, Albers GHR. Low-intensity ultrasound in the treatment of nonunions. J Trauma 2001;51:693 703.
4. Rubin C, Bolander M, Ryaby JP, et al. The use of low-intensity ultrasound to accelerate the healing of fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 2001;83A(2):259 70
You can read more about the Exogen ultrasound bone healing device by visiting www.exogen.com